Geography Notes VIII
Ch.1 Resources
Question 1.
Answer the following questions.
(i) Why are resources distributed unequally over the earth?
(ii) What is resource development?
(iii) Why are human resources important?
(iv) What is sustainable development?
Answer.
(i) Resources are distributed unequally over the’earth because of the different natural conditions, and physical factors like terrain, climate and altitude.
(ii) Resource development is the method of utilising our intelligence in order to improve the quality, usability and utility of a resource.
(iii) Human resources are important because the development of other resources solely depends upon this resource as humans have knowledge, skill, and technology to develop other resources.
(iv) We should use resources in such a balanced way that we satisfy our needs as well as conserve them for the future. This concept is called sustainable development.
Question 2.
Tick the correct answer.
(i) Which one of the following does not make a substance a resource?
(a) utility
(b) value
(c) quantity
(ii) Which one of the following is a human-made resource?
(a) medicines to treat cancer
(b) spring water
(c) tropical forests
(iii) Complete the statement. Biotic resources are
(a) derived from living beings.
(b) made by human beings.
(c) derived from non-living things.
Answer.
(i) (c), (ii) (a), (iii) (a).
Question 3.
Differentiate between the following.
(a) Potential and actual resources
(b) Ubiquitous and localised resources
Answer.
(a)

Question 4.
Activity
“Rahiman paani raakhiye,
Bin paani sab soon.
Paani gaye na ubere Mod, manus, choon…”
[Says Rahim, keep water, as without water there is nothing. Without water pearl, swan and dough cannot exist.] These lines were written by the poet Abdur Rahim Khankhanam, one of the nine gems of Akbar’s court. What kind of resource is the poet referring to? Write in 100 words what would happen if this resource disappeared?
Answer.
The resource referred to by the poet is the water. It is one of the most indispensable resources of life. It can be said to be one of the preconditions of life, like air. Firstly, water serves the most basic purpose of drinking, without which life is not possible. In the absence of water, one would be unable to clean clothes, utensils, or even take a bath. Farmers depend on water for irrigation. Rainwater is so important for proper agriculture. Water is also used in cooking food. Nowadays water has proved to be a useful source of electricity. Besides human beings, plants require water for their growth. Water is also required for various industrial purposes in factories. In short, no form of life can go on without water.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 Resources Exercise Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct option.
(i) Which of these is not a resource?
(a) the Indian Prime Minister
(b) your Geography book
(c) a small piece of paper
(d) none of these
(ii) Which of these does not have economic worth but is valuable?
(a) shoes
(b) mountains
(c) coal
(d) none of these
(iii) The types of resources on basis of stock are
(a) ubiquitous and localised
(b) actual and potential
(c) renewable and non-renewable
(d) abiotic and biotic
(iv) Which of the following is a non-renewable resource?
(a) solar energy
(b) water
(c) soil
(d) natural gas
(v) Which of these is an example of sustainable development?
(a) ignoring the lights when they are switched on but not required
(b) not wasting paper
(c) using coal and petroleum deposits at a fast pace
(d) none of these
Answer.
(i) (d), (ii) (b), (iii) (c), (iv) (d), (v) (b).
Question 2.
Fill in the blank spaces given to complete each sentence.
- A substance becomes a resource if it has …………..
- ………….. and …………. are two important factors which make a substance a resource.
- On the basis of the level of development, resources are classified into ……………. and …………..
- An actual resource to crazy might have been a ……………. resource some time ago.
- Windmills generate …………..energy which is a resource because it will never end up.
- Although renewable resources can be replenished, we should be …………… regarding their use.
- Coal and petroleum are examples of ………….. resources.
- Air is a ubiquitous resource since it is found ………………..
- Physical factors affecting the presence of a localised resource are …………….., ………………, and ……………
- Using resources carefully and giving them time to get renewed is called ………………..
Answer.
- utility
- time, technology
- actual, potential
- potential
- wind, renewable
- careful
- non-renewable
- everywhere
- terrain, altitude, climate
- resource conservation.
Question 3.
State whether each of the following statements is true (T) or false (F).
- We should wastewater since it is a renewable resource and we do not need to be careful in its use.
- A resource always has the same economic value.
- With respect to electricity, water was a potential resource until a few years back.
- All natural sources of energy are renewable.
- A farmer is a human resource.
- Resources need to be conserved for future generations.
- Sustainable development is a way to use resources carefully as well as saving them for the future.
Answer.
- False
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True
- True.
Question 4.
Match the items given in Column I correctly with those given in Column II.
Answer:
(i) (d), (ii) (a), (iii) (e), (iv) (b), (v) (c).
Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 Resources Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the condition for a substance to be called a resource?
Answer:
A substance needs to have some utility to be called a resource.
Question 2.
What do you understand by the word “utility”?
Answer:
If a substance can be used in any way, it is said to have a utility.
Question 3.
What are the natural resources?
Answer:
Resources that are drawn directly from nature are called natural resources.
Question 4.
What is the name given to the type of resources that have limited stock?
Answer:
The resources having limited stock are called non-renewable resources.
Question 5.
How are resources classified according to their distribution?
Answer:
On the basis of their distribution, resources are classified into ubiquitous and localised.
Question 6.
Give three examples of abiotic resources.
Answer:
Air, land, soils.
Question 7.
How are human-made resources different from natural resources?
Answer:
Human-made resources have been created by human beings, whereas natural resources are provided by nature.
Question 8.
What is human resource development?
Answer.
Improving the quality of human skills in order to make them more useful is called human resource development.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 Resources Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the terms of resource conservation and sustainable development.
Answer.
Resource conservation is the concept of using resources carefully so that they do not end up quickly. The future generations also need the resources, but if we keep using them at a fast pace, they may end up, thus posing problems for the future. We should use resources in such a balanced way that we satisfy our needs as well as conserve them for the future. This concept is called sustainable development.
Question 2.
Why are human beings resources?
Answer.
Human beings are intelligent living beings. They can use their intelligence to realise the utility of substances. Had there been no humans, the resources would not have been resources. Human beings are interdependent on each other, and they prove useful to each other. For example, a postman renders us an important service, so he is a resource.
Question 3.
Explain how resources are classified broadly.
Answer.
Resources are broadly classified into natural, human-made and human. Natural resources are those that are taken from nature. They are used without modifying them, i.e. in the same form as they exist in. Rivers, lakes, air, soils, minerals, trees, mountains, etc. are natural resources. Human-made resources have not been provided to us by nature. Human beings have used their intelligence to manufacture them for their own use. Examples include vehicles, buildings, roads, telephones, etc.
Human resources include people who serve us in any way. A teacher, doctor, carpenter, cobbler, etc. are human resources.
Question 4.
Write a short note on the significance of time and technology in making a substance a resource.
Answer.
Time and technology are important factors in making substances resources. With time, technology develops. As technology develops, we begin to discover new ways to make life better. In this process, certain substances which were useless to us earlier become useful. An invention and discovery give us new resources. An example is a hydroelectricity. This technology has made water a source of electricity.
Question 5.
As human beings, how can we ensure sustainable development?
Answer.
Since we live on the earth, it is our duty to practice sustainable development. We can do this by ensuring that:
- The usage of renewable resources is sustainable,
- The diversity of life on earth is maintained,
- The damage caused to nature by our activities is’as Tow as possible.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 Resources Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe how resources are classified.
Answer.
Resources are broadly classified into natural, human-made, and human. Natural resources are those that are taken from nature. They are used without modifying them, i.e. in the same form as they exist in. Rivers, lakes, air, soils, minerals, trees, mountains, etc. are natural resources. Human-made resources have not been provided to us by nature. Human beings have used their intelligence to manufacture them for their own use. Examples include vehicles, buildings, roads, telephones, etc.
Human resources include people who serve us in any way. A teacher, doctor, carpenter, cobbler, etc are human resources.
Ch.2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources
Question 1.
Answer the following questions.
(i) Which are the two main climatic factors responsible for soil formation?
(ii) Write any two reasons for land degradation today.
(iii) Why is land considered an important resource?
(iv) Name any two steps that the government has taken to conserve plants and animals.
(v) Suggest three ways to conserve water.
Answer.
(i) Temperature and rainfall are two main climatic factors responsible for soil formation. Rainfall contributes in breaking the rocks by applying pressure. Temperature fluctuations between hot and cold also form cracks in the rocks.
(ii) Reasons for land degradation are:
- Ever-growing demand of the growing population
- Destruction of forest‘cover
(iii) Land is an important resource because it provides surface for agriculture, living, forestry, industries, construction, etc. Most activities take place on land.
(iv) Steps taken by the government include establishment of natural parks and wildlife sanctuaries in different parts of India. Their purpose is conservation of vegetation and wildlife, respectively.
(v) Three ways to conserve water are as under:
- Rainwater harvesting: It is a method of collecting water while it rains so that it may come of use in the future.
- The canals used for irrigation should be properly built so that loss of water does not take place while the water is transported to the field.
- In dry regions, drip or trickle irrigation is suggested.
Question 2.
Tick the correct answer.
(i) Which one of the following is NOT a factor of soil formation?
(a) time
(b) soil texture
(c) organic matter
(ii) Which one of the following methods is most appropriate to check soil erosion on steep slopes?
(a) shelter belts
(b) mulching
(c) terrace cultivation
(iii) Which one of the following is NOT in favour of the conservation of nature?
(a) switch off the bulb when not in use
(b) close the tap immediately after using
(c) dispose polypacks after shopping
Answer.
(i) (b), (ii) (c), (iii) (c).
Question 3.
Match the followings:
Answer.
(i) (c), (ii) (d), (iii) (a), (iv) (b).
Question 4.
State whether the given statement is true or false. If true, write the reasons.
- Ganga-Brahmaputra plain of India is an overpopulated region.
- Water availability per person in India is declining.
- Rows of trees planted in the coastal areas to check the wind movement is called intercropping.
- Human interference and changes of climate can maintain the ecosystem.
Answer.
- True
- True
- False
- False
Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources Exercise Questions
Question 1.
Multiple Choice Questions Choose the correct option.
(i) Which of these resources covers about three-fourths of the total surface of earth?
(a) land
(b) soil
(c) air
(d) water
(ii) What are low-lying areas very susceptible to?
(a) earthquakes
(b) landslides
(c) flooding
(d) tsunamis
(iii) Which of these physical features are best suited for living?
(a) plains and river valleys
(b) mountains
(c) deserts
(d) lakes and rivers
(iv) Which of these is example of community land?
(a) the Sunderban forests
(b) a bungalow
(c) the Parliament House
(d) none of these
(v) What is the majority of land in India used for?
(a) cultivation
(b) pasture
(c) forests
(d) none of these
(vi) Which of these countries is mainly covered with forest land?
(a) India
(b) Brazil
(c) USA
(d) both b and c
( vii) Due to what feature is ocean water unfit for human consumption?
(a) poisonous
(b) salinity
(c) water temperature
(d) none of these
Answer:
(i)(d), (ii)(c), (iii)(a), (iv)(a), (v)(a), (vi)(d), (vii)(b).
Question 2.
Fill in the blank spaces given to complete each sentence.
- The percentage of fresh water on …………..
- The process responsible for soil formation is called ……………
- Private land is owned‘by a fan ………………
- The grainy layer on land is called …………….
- Soil becomes fertile due to the right mix of …………… and ……….
- The colour, texture, etc of soil is determined by ……………….
- Climate factors influencing rate of weathering include and …………….
- ………….. is the growing of different crops in alternate rows.
- 70% of fresh water exists as ……………..
Answer:
- 2.7
- weathering,
- individual
- soil
- minerals, organic matter
- parent rock
- rainfall, temperature
- intercropping
- ice sheets.
Question 3.
State whether each of the following statements is true (T) or false (F).
- The land has similar features all over the surface of the earth.
- Plains and valleys are densely populated because of soil fertility.
- Population and technology are important factors that determine land use pattern.
- The growing population is not a cause of soil erosion.
- Topography and organic material affect the soil composition of soil.
- Time affects the rate of humus formation during the process of soil formation.
- The earth is called the water planet because of the large amount of water available over it.
- Africa and West Asia are areas facing serious water scarcity.
- Forest and other vegetation promote surface run-off.
- The convention, CITES, lists species which should not be traded.
Answer.
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
- True
- True
- True
- False
- True
Question 4.
Match the items given in Column I correctly with those given in Column II.
Answer.
(i) (c), (ii) (a), (iii) (e), (iv) (b), (v) (d), (vi) (f).
Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the possible reasons behind the uneven distribution of population around the world?
Answer.
The reasons behind uneven population distribution are mainly the varied conditions of land and climate.
Question 2.
Give three common forms of land use.
Answer.
Three common land use forms are: (i) As cropland, (ii) Pasture, (iii) Forests.
Question 3.
What human factors determine land use pattern?
Answer.
Human factors affecting land use pattern are population and technology.
Question 4.
Define soil.
Answer.
The thin layer of grainy substance covering the surface of the earth is called soil.
Question 5.
What is required to make soil fertile?
Answer.
The right mix of minerals and organic matter is needed to make soil fertile.
Question 6.
What is parent rock?
Answer.
The rock from which soil is derived is called parent rock.
Question 7.
What are the factors threatening soil as a resource?
Answer.
Two factors that threaten soil as a resource are soil erosion and its depletion.
Question 8.
What method of soil conservation may be used in coastal and dry reqions?
Answer.
Shelter belts are used to protect the soil in coastal and dry regions.
Question 9.
Why is the earth called the “water planet”?
Answer.
The earth’s surface has about three- fourths water, so it is called “water planet”.
Question 10.
In what forms is fresh water found on the earth?
Answer.
Fresh water is found in the forms of groundwater, water in rivers and lakes, and water vapour.
Question 11 .
What is the name given to the process involved in rain formation?
Answer.
The process involved in the formation of rain is called “water cycle”.
Question 12.
Name some regions of water scarcity in the world.
Answer.
Africa, West Asia, South Asia, parts of western USA, northwest Mexico, parts of South America, and Australia face water scarcity.
Question 13.
Name a method to save surface run-off.
Answer.
Water harvesting is a method to save surface run-off.
Question 14.
How is a bird like vulture important for the ecosystem?
Answer.
A vulture feeds on dead livestock and so it cleanses the environment.
Question 15.
What is the distinguishing feature between evergreen and deciduous forests?
Answer.
Evergreen forests never shed their leaves whereas deciduous forests shed their leaves once a year.
Question 16.
What is the Vanamahotsava?
Answer.
The social programme of planting trees, organized at the community level is called vanamahotsava.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How is land being degraded? Suggest methods to conserve land resource.
Answer.
The ever-growing population has increased demand for living space, due to which forests are being destroyed, thus causing land degradation. The rate of degradation of land resources can be checked by promoting afforestation, land reclamation, regulated use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers, and checking to overgraze.
Question 2.
What is weathering?
Answer.
Weathering refers to the breaking up and decay of exposed rocks. This breaking up and decay are caused by temperature fluctuations between too high and too low, frost action, plants, animals, and even human activity. Weathering is the major process involved in the formation of soil. It takes millions of years to form soil by this process.
Question 3.
How is water an important resource?
Answer.
Water is an indispensable resource of life. Firstly water serves the most basic purpose of drinking, without which life is impossible. It is helpful in cleaning our bodies, clothes, and utensils. Farmers depend on water for irrigation. Water is also used in cooking food. Water is a source of electricity as well. Plants require water for their growth. Water is required for various industrial purposes in factories.
Question 4.
Write a short note on wildlife.
Answer.
The animal kingdom, which consists
of animals, birds, aquatic creatures and insects, is called wildlife. These creatures provide us various important products such as milk, meat, hides, and wool. Bees give us honey and help in pollination. They play the role of decomposers in the environment. Birds like the vulture are scavengers and they help in cleansing the environment. All forms of wildlife are an integral part of our ecosystem.
Question 5.
What are the major types of vegetation in the world? Describe vegetation in different rainfall conditions.
Answer.
The major types of vegetation in the world are grouped as forests, grasslands, scrubs and tundra.” In areas of heavy rain, huge trees can be found. Forests are abundant in areas of heavy rainfall. With moisture and rainfall the density of forests declines. In moderate rainfall areas, grasslands are found. In diy areas, we find thorny shrubs and scrubs. Plants here have deep roots and leaves have thorny surface to reduce loss of moisture. The tundra vegetation consists of mosses and lichens.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 2 Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Resources Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe methods of soil conservation.
Answer.
Some common methods of soil conservation are mentioned below: Mulching. Mulching is the process of covering the bare ground between plants with a layer of organic matter like straw. It contributes in retaining soil moisture.
Terrace Farming. Terrace farming is the method of farming in which broad flat steps or terraces are made on the steep slopes so that flat surfaces are available to grow crops 4 They reduce run-off and soil erosion. Intercropping. In intercropping, different crops are grown in alternate rows and are sown at different times to protect the soil from being washed away by rain.
Contour Ploughing. Ploughing parallel to the contours of a hill slope to form a natural barrier for water to flow down a slope is called contour ploughing.
Shelter Belts. Rows of trees that are planted in certain areas to check wind movement are called shelter belts. Contour Barriers. Stones, grass, and soil are used to build barriers along contours. Trenches are made in front of the barriers to collect water.
Rock Dams. This prevents gullies and further soil loss since rocks are piled up to slow down the flow of water. Q.2. What is the threat to vegetation and wildlife? What is the need to conserve them? How can we do this? [V. Imp.] Ans. Forests and wildlife are an important resource. Climate change and human interferences in the animal kingdom can cause loss of natural habitat for plants and animals. Certain species have become endangered and many have become extinct now.
Poaching incidents contribute to their extinction. Plants and animals are an important part of the ecosystem. Plants provide food, oxygen and shelter to humans and animals. Animals provide us important products such as milk, meat, honey, etc. There exists a balance in the environment if we do not disturb the natural number of species living on the earth. A single extinction can affect the ecosystem badly. So animals and plants obviously need to be conserved. The government has introduced national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and biosphere reserves for this purpose. Poaching should be severely dealt with. Indiscriminate killings need to be discouraged. Social awareness must be created about the importance of trees, social forestry. Students should be involved in vanamahotsavas at regional and community levels
Ch:3 Mineral and Power Resources
Question 1.
Answer the following questions.
(i) Name any three common minerals used by you every day.
(ii) What is an ore? Where are the ores of metallic minerals generally located?
(iii) Name two regions rich in natural gas resources.
(iv) Which sources of energy would you suggest for
(a) rural areas (b) coastal areas (c) arid regions
(v) Give five ways in which you can save energy at home.
Answer:
(i) Three common minerals used by us in day-to-day life are copper, iron and salt.
(ii) Ore is the raw me tat-found in the earth mixed with other materials or impurities.
They are generally located in igneous or metamorphic rocks.
(iii) Two regions in India rich in natural gas resources are Jaisalmer and Krishna-Godavari delta.
(iv) (a) For rural areas, solar energy and wind energy are feasible options. There aren’t many high-rise buildings to act as an obstacle for sunlight or to break the momentum of wind. ”
(b) For coastal areas, wind energy and tidal energy are good choices.
(c) For arid regions, wind energy and solar energy are feasible, for reasons similar to rural areas.
(v) Five ways in which one can save energy at home:
- Promoting the use of solar energy as much as possible.
- Using biogas as cooking fuel.
- Drying clothes in sunlight instead of electric dryers to prevent emissions and unnecessary use of electricity.
- Avoiding misuse of electricity; switching off fans and lights when not required.
- Using pressure cookers for cooking.
Question 2.
Tick the correct Answer:
(i) Which one of the following is not a characteristic of minerals?
(a) They are created by natural processes.
(b) They have a definite chemical composition.
(c) They are inexhaustible.
(d) Their distribution is uneven.
(ii) Which one of the following is not a producer of mica?
(a) Jharkhand
(b) Karnataka
(c) Rajasthan
(d) Andhra Pradesh
(iii) Which one of the following is a leading producer of copper in the world?
(a) Bolivia
(b) Ghana
(c) Chile
(d) Zimbabwe
(iv) Which one of the following practices will not conserve LPG in your kitchen?
(a) Soaking the dal for some time before cooking it.
(b) Cooking food in a pressure cooker.
(c) Keeping the vegetables chopped before lighting the gas for cooking.
(d) Cooking food in an open pan kept on low flame.
Answer:
(i) (c), (ii) (b), (iii) (c), (iv) (d).
Question 3.
Give reasons.
(i) Environmental aspects must be carefully looked into before building huge dams.
(ii) Most industries are concentrated around coal mines.
(iii) Petroleum is referred to as “black gold”.
(iv) Quarrying can become a major environmental concern.
Answer:
(i)
- Because of the following reasons:
- Dams create an imbalance in the earth’s equilibrium.
- Deforestation leads to environmental pollution.
- People are displaced.
- Cities/villages/towns are shifted causing untold hardships to people.
- Flood threats loom large.
- Earthquake threats.
- Silting of lakes a problem.
(ii) Presence of coal mines around industries reduces the costs of transportation and also ensures easy availability of fuel.
(iii) Petroleum is a very valuable fossil fuel. It is used for running all types of machinery, transport vehicles, from a bicycle to an aeroplane.
(iv) After quarrying, pits are not covered so they may cause environmental hazards.
Question 4.
Distinguish between the following.
(i) Conventional and non-conventional sources of energy.
(ii) Biogas and natural gas.
(iii) Ferrous and non-ferrous minerals
(iv) Metallic and non-metallic minerals.
Answer:
(i)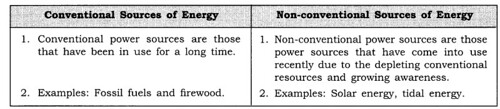



Class 8 Geography Chapter 3 Mineral and Power Resources Exercise Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct option.
(i) Which of these is a non-metallic mineral?
(a) Iron ore
(b) Bauxite
(c) Limestone
(d) Manganese ore
(ii) Which continent produces more than half of the world’s tin?
(a) Africa
(b) Asia
(c) Europe
(d) South America
(iii) Which continent is the leading producer of iron ore in the world?
(a) North America
(b) Asia
(c) Europe
(d) Australia
(iv) Which state is a major bauxite producing area?
(a) Goa
(b) Madhya Pradesh
(c) Assam
(d) Tamil Nadu
(v) What is the name given to the electricity produced from coal?
(a) Nuclear power
(b) Thermal power
(c) Fossil fuel
(d) None of these
(vi) Which of these is a conventional source?
(a) Coal
(b) Petroleum
(c) Natural gas
(d) All of these
(vii) Which of these is called buried sunshine?
(a) Petroleum
(b) Coal
(c) Solar energy
(d) Tidal energy
Answer:
(i) (c), (ii) (b), (iii) (c), (iv) (b), (v) (b), (vi) (d), (vii) (b).
Question 2.
Fill in the blank spaces given to complete each sentence.
- Metallic minerals are classified into …………….. and ………….
- Gold and silver are …………. minerals.
- Minerals can be extracted by ………….,…………., or …………
- Deep bores dug to reach mineral deposits are called …………
- Metallic minerals are generally found in ……….. and…………..rock formations.
- The mineral deposits in North America have located in three zones: …………… the Appalachian region and the mountain ranges of the West.
- …………… is the largest producer of bauxite in the world.
- …………. is the most abundantly available fossil fuel.
- Petroleum is drilled from ………
- Bhakra Nangal is an important …………….. station in India.
- …………… and……… are radioactive metals.
Answer:
- ferrous, non-ferrous
- non-ferrous
- mining, drilling, quarrying
- shafts
- igneous, metamorphic
- the Canadian region north of the Great Lakes
- Australia
- Coal
- Oil fields
- hydel power
- Uranium, thorium.
Question 3.
State whether each of the following statements is true (T) or false (F).
- All ores are rocks but all rocks are not minerals.
- Quarrying is good for the environment.
- Mineral fuels like coal and petroleum are found in sedimentary strata.
- Coal is more predominant in the Canadian Shield Region than the Appalachians.
- Chile and Peru are leading producers of copper.
- Kolar in Karnataka has large deposits of silver.
- Copper is an element used in almost everything.
- Bauxite is the ore of aluminium.
- Nuclear power can be produced from the nuclei of most elements.
Answer:
- Ture
- False
- Ture
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True
- False
Question 4.
Match the items given in Column I correctly with those given in Column II.
Answer:
(i) (d), (ii) (a), (iii) (b), (iv) (c), (v) (e).
Class 8 Geography Chapter 3 Mineral and Power Resources Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Differentiate between a rock and an ore.
Answer:
A rock is an aggregate of one or more minerals. An ore is a rock from which minerals are mined.
Question 2.
Define quarrying.
Answer:
Quarrying is a process of extraction in which minerals lying near the surface are simply dugout.
Question 3.
Name the leading tin producers in Asia.
Answer:
China, Malaysia, and Indonesia are leading tin producers in Asia.
Question 4.
Name two areas in Australia, which have large deposits of gold.
Answer:
Two areas in Western Australia having large deposits of gold are Kalgoorlie and Coolgardie.
Question 5.
Name two minerals in whose production India contributes a significant part.
Answer:
India has vast deposits of high-grade iron ore, and it is also a leading producer of salt.
Question 6.
In which industry is silicon important? From which ore is it obtained?
Answer:
Silicon is important in the computer industry. It is obtained from quartz.
Question 7.
Why are minerals considered non-renewable?
Answer:
Minerals take thousands of years to form. The rate of formation is much smaller than the rate of consumption. So we classify them as non-renewable.
Question 8.
Why is coal called “buried sunshine”?
Answer:
Coal is called “buried sunshine” because it is found buried under the earth, and is as important a source of energy as sunshine.
Question 9.
Why are petroleum and its derivatives called “black gold”?
Answer:
Petroleum and its derivatives are black in colour but as valuable as gold, so we refer to it as “black gold”.
Question 10.
What is natural gas?
Answer:
Natural gas is a fossil fuel obtained with petroleum deposits in oil fields.
Question 11.
Which was the first country to develop hydroelectricity?
Answer:
Norway was the first country to develop hydroelectricity.
Question 12.
Name some important hydel power stations in India.
Answer:
Bhakra Nangal, Gandhi Sagar, Nagaijunasagar, and Damodar Valley Projects are important hydel power stations in India.
Question 13.
Name nuclear power stations in India.
Answer:
Kalpakkam, Tarapur, Ranapratap Sagar, Narora, and Kaiga are the nuclear power stations in India.
Question 14.
Give one advantage of biogas over natural gas.
Answer:
Biogas is a renewable source of energy whereas the amount of natural gas is limited.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 3 Mineral and Power Resources Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name and describe briefly methods of extraction.
Answer:
Mining, drilling, and quarrying are methods of extraction. Mining is a process of extraction of taking out minerals from rocks under the earth’s surface.
- Opencast mining: In this, minerals lying at shallow depths are taken out by removing the surface layer.
- Shaft mining: In this, deep bores (called shafts) are made to reach mineral deposits lying at large depths.
- Drilling: In this, deep wells are bored to take out minerals.
- Quarrying: It is the process of extraction in which minerals lying very close to the surface are extracted just by digging them out.
Question 2.
Where are minerals found?
Answer:
Minerals are found in different types of rocks. Metallic minerals are usually found in igneous and metamorphic rocks that form large plateaus. Examples: iron ore is found in north Sweden, copper, and nickel in Canada. In igneous and metamorphic rocks in South Africa, iron, nickel, chromites, and platinum are found. Non-metallic minerals are found in sedimentary rock formations. Limestone deposits are found in France. Mineral fuels such as coal and petroleum are found in sedimentary strata.
Question 3.
Describe the mineral distribution in North America.
Answer:
The mineral deposits in North America are found in three zones: the Canadian region in the north of the Great Lakes, the Appalachian region, and the Rocky Mountains in the West. Iron ore, nickel, gold, uranium, and copper are mined in the Canadian Shield Region, coal in the Appalachian region. Western Cordilleras have vast deposits of copper, lead, zinc, gold, and silver.
Question 4.
Write common uses of minerals.
Answer:
Minerals are important in many industries. Minerals used in gems are usually very hard. These are then set in varying styles of jewellery. Iron and copper are metals used in almost everything. Copper is present in everything from coins to pipes and electricity wires. Silicon, obtained from the mineral quartz, is the base of the computer industry. Aluminium, obtained from bauxite ore, and its alloys are used in aeroplanes due to their lightweight. Aluminium is also used in kitchen cookware.
Question 5.
How is hydroelectricity, produced?
Answer:
Hydroelectricity is produced from the energy possessed by water falling from great heights. River water is stored in dams. When rainwater or river waterfalls from heights, it flows over turbine blades placed at the bottom of the dam. The moving blades are connected to a generator which produces electricity from this energy. This electricity is called hydroelectricity. The water discharged after its production is used for irrigation.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 3 Mineral and Power Resources Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name and describe some non- conventional sources of energy.
Answer:
Non-conventional power sources are those power sources that have come into use recently due to the depleting conventional resources and growing awareness. Solar energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, nuclear power, and tidal energy are examples of non- conventional power sources.
Solar energy is the heat and light energy captured from the sun. Solar cells help to convert this energy to electricity. Solar energy is used in solar heaters, solar cookers, solar dryers, etc.
Wind energy is the energy possessed by moving air (wind). Windmills are used to convert wind energy to electricity. Wind farms having clusters of windmills located in coastal regions and mountain passes.
Nuclear power is the energy possessed by the nuclei of atoms of naturally occurring radioactive elements like uranium-, thorium, etc.
Geothermal energy is the heat energy obtained from the inside of the earth. The temperature inside the earth increases as we go deeper. This heat is used to produce electricity. It is accessed in the form of hot springs. Tidal energy is the energy generated from tides. It is harnessed by building dams at narrow openings of the sea.
Biogas is a gaseous fuel obtained from the decomposition of organic waste like dead plant and animal material or animal dung and kitchen waste. It is an excellent fuel for cooking and lighting and is environment-friendly.
Question 2.
Write the advantages and dis¬advantages of non-conventional sources of energy.
Answer:
Advantages:
- Non-conventional sources of energy are usually inexhaustible. They do not pollute the environment.
- Nuclear power is emitted in large amounts.
- Most non-conventional sources of energy cost less.
- These forms of energy are safe to use and clean.
Disadvantages:
- Windmills are costly to set up. So using them to harness wind energy is costly, even though the electricity generated from it is cheap.
- Setting up windmills disturbs radio and TV broadcasts.
- Harnessing tidal energy destroys the natural habitats of wildlife.
- Moreover, tidal energy is difficult to harness.
- Obtaining nuclear energy from radioactive material generates radioactive waste. It is expensive too.
- Biogas, although useful and renew¬able, contributes to the greenhouse effect.
Ch:4 Agriculture
Question 1.
Answer the following questions.
(i) What is agriculture?
(ii) Name the factors influencing agriculture.
(iii) What is shifting cultivation? What are its disadvantages?
(iv) What is plantation agriculture?
(v) Name the fibre crops and name the climatic conditions required for their growth.
Answer:
(i) Agriculture is the primary activity that involves the cultivation of crops, fruits, vegetables, flowers and rearing of livestock.
(ii) Factors influencing agriculture include the topography of soil and climate.
(iii) Shifting cultivation is the type of farming in which agricultural activities are shifted from one field to another when the fertility of the soil of the former is diminished
Disadvantages:
- Deforestation
- Soil erosion
- Small patches for cultivation
- Not sufficient for feeding a large population.
(iv) Plantation agriculture is a type of commercial farming where only a single crop (like tea, coffee, sugarcane, cashew, rubber, banana or cotton) is grown. A large amount of labour and capital are required. The product is processed on the farm itself or nearby factories.
(v) Two major fiber crops are jute and cotton. Jute grows well on alluvial soil and requires high temperature, heavy rainfall, and a humid climate for its growth. Cotton needs high temperatures, light rainfall, and bright sunshine for its proper growth.
Question 2.
Tick the correct Answer:
(i) Horticulture means
(a) growing of fruits and vegetables
(b) primitive farming
(c) growing of wheat
(ii) Golden fiber refers to
(a) tea
(b) cotton
(c) jute
(iii) Leading producers of coffee
(a) Brazil
(b) India
(c) Russiac
Answer:
(i) (a), (ii) (c), (iii) (a).
Question 3.
Give reasons.
(i) In India agriculture is a primary activity.
(ii) Different crops are grown in different regions.
Answer:
(i) Agriculture is an activity of growing crops, fruits, vegetables, flowers, and rearing of livestock. It is a primary activity since it directly involves natural resources. In India, a huge number of people derive the activity from their ancestors. Due to lack of literacy in general, farmers prefer agriculture since they acquire the required skills from their ancestors, and so feel comfortable with it.
(ii)
- Different topography
- Different soils
- Different climates
- Different lifestyles of the people in different regions.
Question 4.
Distinguish between the following.
(i) Primary activities and secondary activities.
(ii) Subsistence farming and intensive farming.
Answer:
(i)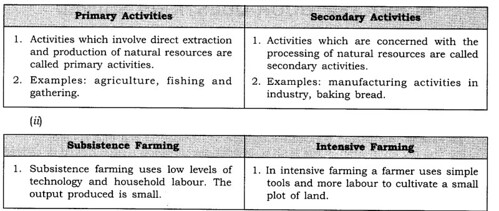
Question 5.
Find out the difference between the lifestyle of farmers in the USA and India on the basis of pictures collected from magazines, books, newspapers and the internet.
Answer:
The lifestyle of an Indian farmer is quite different from that of a farmer in the USA. An Indian farmer does not have much land whereas the average size of a farm in the USA is about 250 hectares. An Indian farmer lives in his house but an American farmer lives in his farm. A farmer in India applies his own experience, and advice of other farmers and elders regarding farming practices. But a farmer in the USA gets his soil tested in laboratories to assess the nutrients of the soil. An Indian farmer does not know of any technical advancements whereas a farmer in the USA has a computer which is linked to the satellite. In comparison to an Indian farmer, an American farmer is much more advanced in every aspect.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture Exercise Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct option
(i) Which of these is a tertiary activity?
(a) manufacturing wool
(b) selling grocery
(c) agriculture
(d) none of these
(ii) What is the breeding of fish known as?
(a) agriculture
(b) pisciculture
(c) sericulture
(d) viticulture
(iii) What is the main crop in intensive subsistence agriculture?
(a) rice
(b) maize
(c) wheat
(d) oilseeds
(iv) Which form of farming is also called “slash and bum” agriculture?
(a) subsistence farming
(b) shifting cultivation
(c) plantation
(d) mixed farming
(v) Which of these is not a plantation product?
(a) rubber
(b) coffee
(c) rice
(d) tea
(vi) In what season is wheat grown in India?
(a) summer
(b) winter
(c) monsoon
(d) autumn
(vii) Name the staple diet of tropical and sub-tropical regions.
(a) wheat
(b) rice
(c)jute
(d) coffee
Answer:
(i) (b), (ii) (b), (iii) (a), (iv) (b),
(v) (c), (vi) (b), (vii) (b).
Question 2.
Fill in the blank spaces given to complete each sentence.
- In the world, ………. percent of the population is engaged in agriculture.
- …………. is the commercial rearing of silkworms.
- ………. and …………… are two fundamental types of farming.
- In the thickly populated areas of monsoon regions of Asia, the major class of farming done is ……………..
- …………, ………….., ………….. and …………. are animals usually reared by nomadic herders.
- In ………., the land is used for growing food and fodder crops and rearing livestock.
- ………….. and ……….. are fibre crops.
- Tea is a major…………… crop in India.
- Wheat thrives best in ……………. soil.
- The three major millets in India are ………….. and ………..
Answer:
- 50
- Sericulture
- Subsistence farming and commercial farming
- intensive subsistence farming
- Yak, sheep, goat, camel
- mixed farming
- Cotton, jute
- plantation
- loamy
- jowar, bajra, ragi
Question 3.
State whether each of the following statements is true (T) or false (F).
- Favourable topography of soil and climate is vital for agriculture.
- Household labour is involved in subsistence farming.
- A transport network is significant for plantation agriculture.
- Major plantations are found in tundra regions.
- In the USA, the farmer usually resides on the farm.
Answer:
- True
- True
- True
- False
- True
Question 4.
Match the items given in Column I correctly with those given in Column II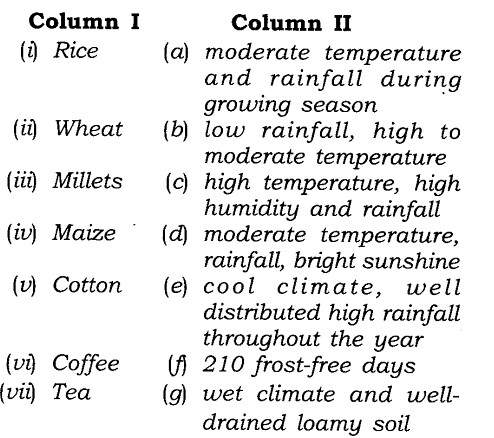
Answer:
(i) (c), (ii) (a), (iii) (b), (iv) (d), (v) (j), (vi) (g), (vii) (e).
Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the basic function of the three basic types of economic activities?
Answer:
The three types of economic activities are involved in the transformation from a plant to a finished product.
Question 2.
What are the tertiary activities?
Answer:
Tertiary activities are those which provide support to primary and secondary activities.
Question 3.
In what sorts of areas are agricultural activities concentrated?
Answer:
Agricultural activities are concentrated in those areas of the world which have suitable conditions of growing crops.
Question 4.
What is arable land?
Answer:
The land on which crops are grown is called arable land.
Question 5.
How is subsistence farming classified?
Answer:
Subsistence farming is classified into intensive and primitive subsistence agriculture.
Question 6.
In what sort of areas is nomadic herding practised?
Answer:
Nomadic herding is practised in semi-arid and arid regions of Sahara, Central Asia, and some parts of India.
Question 7.
Why is mixed farming called so?
Answer:
In mixed farming, the land is used for growing crops as well as rearing livestock.
Question 8.
What is the main feature of plantation agriculture?
Answer:
In plantation agriculture, only a single crop is grown.
Question 9.
What weather conditions are required in the growing and harvesting seasons of wheat?
Answer:
In the growing season, wheat requires moderate temperature and rainfall and in the harvesting season, it needs bright sunshine.
Question 10.
Which two countries lead in the production of jute?
Answer:
India and Bangladesh are the leading producers of jute.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write a short note on the types of economic activities. Give examples.
Answer:
The three types of economic activities are primary, secondary, and tertiary. Primary Activities. Activities which involve direct extraction and production of natural resources are called primary activities. Examples: agriculture, fishing, mining. Secondary Activities. Activities which are concerned with the processing of natural resources are called secondary activities. Examples: manufacturing of finished products. Tertiary Activities. Activities which fall neither in the primary category nor the second category are called tertiary activities. They form support to primary and secondary activities. Examples: selling goods, advertising, and banking.
Question 2.
Name the inputs and outputs of agriculture in general. Also mention the various operations involved.
Answer:
The inputs in agriculture are seeds, fertilisers, machinery, labour, etc. The operations involved in agriculture are ploughing, sowing, irrigation, weeding, and harvesting. As outputs of the farming activity, a farmer gets crops, wool, dairy products, and poultry products.
Question 3.
Explain shifting cultivation.
Answer:
Shifting cultivation is a class of primitive subsistence agriculture. In this, a plot of land is cleared by the farmer. This is done by felling the trees and burning them. The ashes are then mixed with soil and crops are grown. After some time, the land is abandoned and the farmer moves to a different place. This type of farming is common in the thickly forested areas of the Amazon basin, tropical Africa, parts of south-east Asia, and north-east India. It is also called “slash and burn” agriculture, because of the process of felling and burning the trees is involved.
Question 4.
Enlist the climate conditions required for the proper cultivation of rice. Mention the main regions of its production.
Answer:
Rice is a major food crop‘in tropical and sub-tropical parts of the world. Its cultivation needs high temperatures, high humidity and rainfall. Its growth is best in alluvial clayey soils since they have water retention capacity. China and India are the leading producers in the world. In favourable climatic conditions, even two to three crops are grown in a year.
Question 5.
What do you understand by agricultural development?
Answer:
Agricultural development refers to efforts made to increase production in farms so as to meet the ever¬growing demand of the population. The activities that come under this development are increasing the cropped area, growing more crops, improving irrigation, using fertilizers, sowing HYV (high-yielding variety) of seeds, and promoting mechanization. Mechanization ensures that little labor is done by the farmers; instead, machines are used to provide efficiency.
Class 8 Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe subsistence farming and its types in detail.
Answer:
The two main types of farming are:
subsistence farming and commercial farming.
Subsistence farming is practised solely to meet the needs of the farmer’s family. Therefore, the practices involved are usually old- fashioned. Use of modern technology is minimum and most work is done by household labour.
In intensive, subsistence agriculture, simple tools and huge labour are used by a farmer to cultivate a small plot of land. More than one crop is grown annually in favourable conditions. Rice is the major crop. This form of agriculture is seen in the thickly populated areas of the monsoon regions of south, south-east and east Asia. Shifting cultivation is a class of primitive subsistence agriculture. In this, a plot of land is cleared by felling the trees and burning them.
The ashes are then mixed with soil and crops are grown. After some time, the land is abandoned and the farmers move to a different place. This type of farming is common in the thickly forested areas of the Amazon basin, tropical Africa, parts of south-east Asia and north-east India. It is also called “slash and burn” agriculture.
Nomadic herding refers to the practice in which herdsmen move from place to place with their animals for fodder and water. Animals usually reared are the yak, sheep, camel and goats.
Question 2.
Describe commercial farming and its types in detail.
Answer:
Commercial farming is the practice in which crops are grown exclusively for commercial purpose, i.e. for sale in the market. A large area is cultivated and huge capital is involved unlike subsistence farming. Machines are used to a large extent.
Commercial grain farming is a class of commercial farming. Crops like wheat and maize are grown for commercial purpose. The temperate grasslands of North America, Europe and Asia are some common areas where it is seen.
Mixed farming is another type of commercial farming. The land is used for growing food and fodder crops and rearing livestock. Some areas where it is followed are Europe, eastern USA, Argentina, south-east Australia, New Zealand and South Africa. Plantations are a type of commercial farming where only a single crop (like tea, coffee, sugarcane, cashew, rubber, banana or cotton) is grown. Large amount of labour and capital are required. The produce is processed in the farm itself or nearby factories.
Comments
Post a Comment