Science Notes VIII
Chapter no. 1 all notes (science)
1.CROP PRODUCTION AND MANAGMENT
Question 1.
Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks.
float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called _____
(b) The first step before growing crops is _______ of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would ______ on top of the water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and ______ and ______ from the soil are essential.
(a) crop
(b) preparation
(c) float
(d) water, nutrients
Question 2.
Match items in column A with those in column B.
A B
(i) Kharif crops (a) Food for cattle
(ii) Rabi crops (b) Urea and superphosphate
(iii) Chemical fertilisers (c) Animal excreta, cow dung, urine and plant waste
(iv) Organic manure (d) Wheat, gram, pea
(e) Paddy and maize
Answer:
(i) (e)
(ii) (d)
(iii) (b)
(iv) (c)
Question 3.
Give two examples of each.
(a) Kharif crop
(b) Rabi crop
Answer:
(a) Kharif crop: Paddy and maize
(b) Rabi crop: Wheat and gram
Question 4.
Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following.
(a) Preparation of soil
(b) Sowing
(c) Weeding
(d) Threshing
(a) Preparation of soil: Soil preparation is necessary before growing a crop. It involves tilling and loosening the soil. This allows the roots to penetrate deep in the soil and to breath easily even when they are deep.
(b) Sowing: The process of putting seeds into the soil is called sowing. The tool used traditionally for sowing seeds is funnel-shaped. Nowadays a seed drill is used for sowing with the help of tractors. This tool sows the seed uniformly at a proper distance and depth.
(c) Weeding: Some undesirable plants grow along with crop and these unwanted plants are called weeds. The process of removing these unwanted plants is called weeding.
(d) Threshing: The process of separating the grain seeds from the chaff is called threshing.
Question 5.
Explain how fertilisers are different from manure.
Answer:
Fertilisers Manures
(i) A fertiliser is an inorganic salt. (i) Manure is a natural substance obtained by the decomposition of cattle dung, human waste and plant residues.
(ii) A fertiliser is prepared in factories. (ii) Manure can be prepared in the fields.
(iii) A fertiliser does not provide any humus to the soil. (iii) Manure provides a lot of humus to the soil.
(iv) Fertilisers are very rich in plant nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. (iv) Manure is relatively less rich in plant nutrients.
Fertilisers Manures
(i) A fertiliser is an inorganic salt. (i) Manure is a natural substance obtained by the decomposition of cattle dung, human waste and plant residues.
(ii) A fertiliser is prepared in factories. (ii) Manure can be prepared in the fields.
(iii) A fertiliser does not provide any humus to the soil. (iii) Manure provides a lot of humus to the soil.
(iv) Fertilisers are very rich in plant nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. (iv) Manure is relatively less rich in plant nutrients.
Question 6.
What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water.
Answer:
The artificial method of watering the plants for assisting in their growth is called irrigation. Main sources of irrigation are wells, tube-wells, ponds, lakes, rivers.
Two methods which help us to conserve water are:
(i) Sprinkler irrigation system: This irrigation system has an arrangement of vertical pipes with rotating nozzles on the top. It is more useful in the uneven and sandy land where sufficient water is not available.
(ii) Drip irrigation system: This irrigation system has an arrangement of pipes or tubes with very small holes in them to water plants drop by drop just at the base of the root. It is very efficient as water is not wasted at all.
Question 7.
If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Answer:
Wheat crop is sown from November/December to March/April. It is grown in winter and requires less water. If wheat is sown in Kharif season, its production will be decreased considerably.
Question 8.
Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Answer:
Continuous plantation of crops makes the soil poorer in certain nutrients as the crops take up nutrients from the soil. The soil becomes infertile. It does not get enough time to replenish the nutrients.
Question 9.
What are the weeds? How can we control them?
Answer:
The undesirable and unwanted plants which grow naturally along with the crop are called weeds. The growth of weeds can be controlled by adopting many ways. Tilling before sowing of crops helps in the uprooting and killing of weeds, which may then dry up and get mixed with the soil. Weeds are also controlled by using certain chemicals, called weedicides. Weedicides are sprayed in the fields to kill the weeds.
Question 10.
Arrange the following boxes in the proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production.
Crop Production and Management Class 8 Science NCERT Textbook Questions Q10
Answer:
Crop Production and Management Class 8 Science NCERT Textbook Questions Q10.1
Question 11.
Complete the following word puzzle with the help of clues given below.
Down
1. Providing water to the crops.
2. Keeping crop grains for a long time under proper conditions.
5. Certain plants of the same kind grown on a large scale.
Across
3. A machine used for cutting the matured crop.
4. A rabi crop that is also one of the pulses.
6. A process of separating the grain from the chaff.
Answer:
Chapter 2:
Microorganisms – Friend and Foe
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks.
(a) Microovrganisms can be seen with the help of a _____
(b) Blue-green algae fix ______ directly from the air to enhance the fertility of soil.
(c) Alcohol is produced with the help of _____
(d) Cholera is caused by ______
Answer:
(a) microscope
(b) nitrogen
(c) yeast
(d) bacteria
Question 2.
Tick the correct answer.
(a) Yeast is used in the production of
(i) sugar
(ii) alcohol
(iii) hydrochloric acid
(iv) oxygen
Answer:
(ii) alcohol
(b) The following is an antibiotic:
(i) sodium bicarbonate
(ii) streptomycin
(iii) alcohol
(iv) yeast
Answer:
(ii) streptomycin
(c) Carrier of malaria-causing protozoan is:
(i) female Anopheles mosquito
(ii) cockroach
(iii) housefly
(iv) butterfly
Answer:
(i) female Anopheles mosquito
(d) The most common carrier of communicable diseases is
(i) ant
(ii) housefly
(iii) dragonfly
(iv) spider
Answer:
(ii) housefly
(e) The bread or idli dough rises because of:
(i) heat
(ii) grinding
(iii) growth of yeast cells
(iv) kneading
Answer:
(iii) growth of yeast cells
(f) The process of conversion of sugar into alcohol is called
(i) nitrogen fixation
(ii) moulding
(iii) fermentation
(iv) infection
Answer:
(iii) fermentation
Question 3.
Match the organisms in column A with their action in column B.
A | B |
(i) Bacteria | (a) Fixing nitrogen |
(ii) Rhizobium | (b) Setting of curd |
(iii) Lactobacillus | (c) Baking of bread |
(iv) Yeast | (d) Causing malaria |
(v) A protozoan | (e) Causing cholera |
(vi) A virus | (f) Causing AIDS |
(g) Producing antibodies |
Answer:
(i) (e)
(ii) (a)
(iii) (b)
(iv) (c)
(v) (d)
(vi) (f)
Question 4.
Can microorganisms be seen with the naked eye? If not, how can they be seen?
Answer:
The microorganisms cannot be seen with our naked eyes because they are very small in size. Some of these, such as fungus growing on bread, can be seen with a magnifying glass. Others cannot be seen without the help of a microscope.
Question 5.
What are the major groups of microorganisms?
Answer:
Microorganisms are classified on the basis of their size into four major groups. These groups are:
(a) Bacteria
(b) Fungi
(c) Protozoa
(d) Some algae
Question 6.
Name the microorganisms which can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.
Answer:
Rhizobium, Clostridium and Azotobacter.
Question 7.
Write 10 lines on the usefulness of microorganisms in our lives.
Answer:
Microorganisms are useful to us in many ways. For example,
· Bacteria like Lactobacillus convert milk into curd.
· Bacteria are also involved in the making of cheese.
· Acetobacter aceti is used for producing acetic acid from alcohol.
· Yeast is used in the commercial production of alcohol, wine and bakery products.
· Some specific microorganisms are helpful in manufacturing of antibiotics.
· Microorganisms act as cleansing agents and decompose the waste products into manure.
· Dead or weakened microbes are used in the preparation of vaccines.
· Some bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen and increase soil fertility.
· Algae, yeast, fungi or bacteria may be used as an ingredient or a substitute for protein-rich foods that are suitable for human or animal consumption.
· Some microorganisms are taken as probiotics, that are believed to provide health benefits when consumed.
Question 8.
Write a short paragraph on the harms caused by microorganisms.
Answer:
Microorganisms are harmful to us in many ways. For example, microorganisms, called pathogens cause disease in humans, plants and animals. Pathogens or germs enter a healthy body through air, water, contaminated food and infected person by direct or indirect contact or by the carrier. Common ailments like cold, influenza (flu), cough, polio, chicken pox are caused by viruses. Foot and mouth diseases in the cattle are also caused by viruses. Typhoid, tuberculosis (TB) are caused by bacteria. Anthrax a dangerous human and cattle diseases is also caused by bacteria.
Diseases like dysentery and malaria are caused by protozoa. Ringworm is caused by fungi. Several microbes causes diseases in plants and thus reduces the yield. Citrus canker, a bacterial disease, affects trees of citrus fruit and is spread by air. Bhendi yellow vein mosaic disease is caused by a virus and is spread by insects in lady fingers. Rust of wheat is a fungal disease spread through air. Microorganisms that grow on our food sometimes produce toxic substances. These make the food poisonous causing serious illness and even death. This food-borne illness is called food poisoning.
Question 9.
What are antibiotics? What precautions must be taken while taking antibiotics?
Answer:
Antibiotics are the medicines which kill or stop the growth of the disease-causing microbes. They are manufactured by growing specific microorganisms. They are used to cure a variety of diseases.
It is important to take antibiotic only on the advice of a qualified doctor. One must finish the course prescribed by the doctor to make the drug more effective. Antibiotics must not be taken unnecessarily because it may kill beneficial bacteria also. Antibiotics are, however, not effective against cold and flu as they are caused by viruses.
Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Class 8 Science NCERT Intext Activities Solved
Activity 1 (NCERT Textbook, Page 17)
Collect some moist soil from the field in a beaker and add water to it. After the soil particles have settled down, observe a drop of water from the beaker under a microscope. What do you see?
Solution:
It is observed that some tiny organisms are moving around.
Activity 2 (NCERT Textbook, Page 17)
Take a few drops of water from a pond. Spread on a glass slide and observe through a microscope.
Solution:
It is observed that some tiny organisms are moving around.
Activity 3 (NCERT Textbook, Page 20)
Jake 1/2 kg flour (atta or maida), add some sugar and mix with warm water. Add a small amount of yeast powder and knead to make a soft dough. What do you observe after two hours? Did you find the dough rising?
Solution:
It is observed that the dough begins to rise up in volume. Yeast reproduces rapidly and releases C02 during respiration. Etubble of this gas fill the dough and increase its volume.
Activity 4 (NCERT Textbook, Page 20)
Take 500 ml. beaker filled upto 3/4 with water. Dissolve 2-3 teaspoons of sugars in it. Add half a spoon of yeast powder to the sugar solution. Keep it covered in a warm place for 4-5 hours. Now smell the solution. Can you get a smell?
Solution:
It is observed that the solution smell like alcohol. This process of conversion of sugar in alcohol is known as fermentation.
Activity 5 (NCERT Textbook, Page 22)
Take two pots and fill each pot half with soil. Mark them A and B. Put plant waste in pot A and things like polythene bags, empty glass bottles and broken plastic toys in pot B. Put the pots aside. Observe them after 3-4 weeks.
Solution:
It is observed that plant waste in pot A has been decomposed, whereas the polythene bags, empty glass bottles and broken plastic toys in pot B did not undergo such changes.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 – 1 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Name the bacteria responsible for the disease typhoid. [MSE (Chandigarh) 2008]
Answer:
Salmonella typhi.
Question 2.
Chicken pox is caused by ………. virus. [KVS 2008]
Answer:
Varicella zoster.
Question 3.
………….. (disease) is caused by mycoplasma. [KVS 2008]
Answer:
Pleuropneumonia.
Question 4.
Name the toxin released by T.B. bacteria.[MSE (Chandigarh) 2007]
Answer:
Tuberculin toxin is released by T.B. bacteria.
Question 5.
Which microorganism is the cause of malaria ? [NCT 2006]
Answer:
A Protozoan, Plasmodium.
Question 6.
Write two diseases caused by bacteria. [NCT2005]
Answer:
Two diseases caused by bacteria are tuberculosis and diphtheria.
Question 7.
Name any two items that are prepared by using yeast. [KVS 2005]
Answer:
Yeast is used to prepare bread and alcohol.
Question 8.
Fill in the blanks : [NCERT]
1. Microorganisms can be seen with the help of a …………..
2. Blue-green algae fix ………… directly from air to enhance fertility of soil.
3. Alcohol is produced with the help of ………….
4. Cholera is caused by ……………
Answer:
1. Microscope
2. Nitrogen
3. Yeast
4. Bacteria.
Question 9.
Tick the correct answer : [NCERT]
· (a) Yeast is used in the production of
(i) sugar
(ii) alcohol
(iii) hydrochloric acid
(iv) oxygen.
· (b) The following is an antibiotic
(i) Sodium bicarbonate
(ii) Streptomycin
(iii) Alcohol
(iv) Yeast.
· (c) Carrier of malaria-causing protozoan is
(i) female anopheles mosquito
(ii) cockroach
(iii) housefly
(iv) Butterfly.
· (d) The most common carrier of communicable diseases is
(i) ant
(ii) housefly
(iii) dragonfly
(iv) spider.
· (e) The bread or idli dough rises because of
(i) heat
(ii) grinding
(iii) growth of yeast cells
(iv) kneading.
· (f) The process of conversion of sugar into alcohol is called
(i) nitrogen fixation
(ii) moulding
(iii) fermentation
(iv) infection.
Answer:
(a) —> (ii)
(b) —> (ii)
(c) —> (i)
(d) —> (ii)
(e) —> (iii)
(f) —> (iii)
Question 10.
Match the organisms in Column I with their action in Column II. [NCT2010, NCERT]
Column I | Column II |
(a) Bacteria | (i) Fixing nitrogen |
Answer:
Column I | Column II |
(a) Bacteria | (i) Causing cholera |
Question 11.
Name the microorganisms which can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil. [NCERT]
Answer:
Rhizobium, Clostridium md Azotobacter fix atmospheric nitrogen.
Question 12.
Can microorganisms be seen with the naked eye ? If not, how can they be seen ? [NCERT]
Answer:
No, microorganisms cannot be seen with the naked eye. They can only be seen with the help of microscope.
Question 13.
What are the major groups of microorganisms ? [NCERT]
Answer:
· Bacteria
· Fungi
· Protozoa
· Algae.
Question 14.
What are microorganisms ?
Answer:
Microorganisms are organisms that are so small that they can only be seen through a microscope.
Question 15.
Name two diseases caused by viruses.
Answer:
Influenza and cough.
Question 16.
Name two diseases caused by protozoans.
Answer:
Dysentery and malaria.
Question 17.
Which microorganisms are unicellular ?
Answer:
Bacteria and protozoa are unicellular.
Question 18.
Name two multicellular microorganisms.
Answer:
Algae and fungi are multicellular.
Question 19.
Name the bacterium used for production of acetic acid from alcohol.
Answer:
Acetobacter aceti.
Question 20.
Define fermentation.
Answer:
The process of conversion of sugar into alcohol is called fermentation.
Question 21.
Why antibiotics are not effective against cold and flu ?
Answer:
Cold and flu are caused by viruses, so the antibiotics are not effective against them.
Question 22.
What are antibodies ?
Answer:
When a disease carrying microbe enters our body, the body produces antibodies to fight the invader.
Question 23.
Name two diseases which can be prevented by vaccination.
Answer:
Cholera and tuberculosis can be prevented by vaccination.
Question 24.
Name the diseases for which oral drops are given as vaccination.
Answer:
Polio.
Question 25.
What are biological nitrogen fixers ?
Answer:
Some bacteria and blue-green algae are able to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere to enrich soil with nitrogen and increase fertility, are known as biological nitrogen fixers.
Question 26.
What are pathogens ?
Answer:
Diseases-causing microorganisms are called pathogens.
Question 27.
What are communicable diseases ?
Answer:
Microbial diseases which can spread from an infected person to a healthy person through air, water, food or physical contact are known as communicable diseases.
Question 28.
Name two communicable diseases.
Answer:
Chicken pox and tuberculosis.
Question 29.
Name two carriers of disease-causing microbes.
Answer:
Housefly and female Anopheles mosquito.
Question 30.
Name the causative microorganism of tuberculosis and its mode of transmission.
Answer:
Causative microorganisms – Bacteria.
Mode of transmission – Air.
Question 31.
How are cholera and typhoid transmitted ?
Answer:
Cholera is transmitted through water or food.
Typhoid is transmitted through water.
Question 32.
Which microorganism causes foot and mouth disease of cattle ?
Answer:
Virus.
Question 33.
Name one plant disease caused by bacteria and its mode of transmission.
Answer:
Citrus canker is caused by bacteria and transmitted through air
Question 34.
Name one plant disease transmitted by insects and caused by virus.
Answer:
Yellow vein mosaic of bhindi.
Question 35.
Name one plant disease caused by fungi and its mode of transmission.
Answer:
Rust of wheat. It is transmitted through air and seeds.
Question 36.
What is meant by food poisoning ?
Answer:
Food poisoning is caused by consuming food that has bean spoilt by some microorganisms.
Question 37.
What are preservatives ?
Answer:
Chemicals (salts, etc.) that check the growth of microorganisms are called preservatives.
Question 38.
How are pickles preserved ?
Answer:
Pickles are preserved by adding salt or acid.
Question 39.
Name the chemicals used to preserve jams and squashes.
Answer:
Sodium benzoate and sodium metabisulphite are added to jams and squashes to preserve them.
Question 40.
How are meat and fish preserved ?
Answer:
Meat and fish are preserved by covering them with dry salt to check the growth of bacteria.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 – 2 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Describe the role of blue-green algae in fertility of soil. [KVS 2006, MSE (Chandigarh) 2008]
Answer:
Blue-green, algae, also called cyanobacteria, can fix atmospheric nitrogen into usable , compounds. These are then used as fertilizers.
Question 2.
Name three habitats of microorganisms. [MSE (Chandigarh) 2008, 2006]
Answer:
Microorganisms are present in soil, water, outer space and inside the body of animals.
Question 3.
Name the bacterium found in the roots of pea plant. How is this bacterium useful for human beings ? [NCT2007]
Answer:
Rhizobium is the bacterium found in the roots of pea plant. The. bacterium absorbs the atmospheric nitrogen and converts it to nitrates.
Question 4.
What is a vaccine ? Why is it important to vaccinate small children ? [DAV2006]
Answer:
Vaccine is prepared from weak or dead disease-causing microbe. Vaccine is given to healthy persons to prevent occurrence of disease. It is important to vaccinate small children because it creates antibodies in blood.
Question 5.
1. Give full form of ORS.
2. What is vaccination ? [DAV2007]
Answer:
1. ORS — Oral Rehydration Solution.
2. Vaccination is a method to immunise the body against diseases by making the body’s immune system produce antibodies against the disease-causing microbe in the vaccine.
Question 6.
Mention two important uses of fungi. [KVS 2006]
Answer:
Uses of fungi:
· They convert dead organic matter into simple soluble minerals and gases, which can be used again by plants.
· Fungi like yeast is used in bread, beer and wine.
Question 7.
How is pasteurised milk obtained ? [NCT 2010]
Answer:
In pasteurisation, the milk is heated to 62.5°C for 30 minutes or to 71.5°C for 15 seconds. It is then rapidly cooled to 10°C and packed in airtight containers.
Question 8.
Draw a neat and well-labelled diagram of Spirogyra.
Answer:
Question 9.
Draw a labelled diagram of Rhizopus.
Answer:
Question 10.
Draw a labelled diagram of Chlamydomonas. [DAV 1997]
Answer:
Question 11.
Draw a labelled diagram of Amoeba.
Answer:
Question 12.
How are viruses different from other microorganisms ?
Answer:
Viruses reproduce only inside the host organisms that is, bacterial, plant or animal cell.
Question 13.
Give two examples where microorganisms are useful at home.
Answer:
At home microorganisms are used for preparation of curd and cakes.
Question 14.
How are microorganisms useful commercially ?
Answer:
Microorganisms are used for the large scale production of alcohol, wine and acetic acid (vinegar).
Question 15.
How do microorganisms clean the environment ?
Answer:
Microorganisms degrade the harmful substances and clean the environment.
Question 16.
How can we prevent a person from getting Hepatitis B ?
Answer:
· By giving boiled water for drinking.
· By vaccination.
Question 17.
Name one disease caused by bacteria and one disease caused by virus in cattle.
Answer:
· Bacteria – Anthrax.
· Virus – Foot and mouth disease.
Question 18.
How can we control plant diseases ?
Answer:
Plant diseases can be controlled by chemicals which kill the microbes.
Question 19.
Why do we use oil and vinegar to preserve vegetables and fruits ?
Answer:
Use of oil and vinegar prevents spoilage of vegetables and fruits because bacteria cannot live in such an environment.
Question 20.
Why do we keep milk in the refrigerator during summers ?
Answer:
The low temperature in the refrigerator inhibits the growth of microbes.
Question 21.
Why do we boil milk before storing ?
Answer:
Boiling kills the microorganisms.
Question 22.
How are dry fruits preserved ?
Answer:
Dry fruits are preserved by keeping them sealed in airtight packets to prevent the attack of microbes.
Question 23.
Draw a well-labelled diagram of Paramecium.
Answer:
Question 24.
Draw a labelled diagram of Penicillium.
Answer:
Question 25.
· Name the scientist who discovered the vaccine for smallpox.
· Who discovered the bacterium which causes anthrax disease ?
Answer:
· Edward Jenner
· Robert Koch
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 – 3 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
· Tuberculosis is a highly infectious disease. Justify the statement.
· Which vitamin helps in the prevention of common cold ? [MSE (Chandigarh) 2008]
Answer:
· Tuberculosis is a highly infectious disease. TB is transmitted through minute droplets of infected sputum on phelgm, by drinking milk of an infected animal.
· Common cold is prevented by taking vitamin C.
Question 2.
Draw a labelled diagram of virus. [KVS 2008, DAV 2006]
Answer:
Question 3.
Can you store pickles in iron containers ? Why ? [KVS 2007]
Answer:
We can not store pickles in iron containers because the acid present in the pickles reacts with iron. This can cause food poisoning, if consumed.
Question 4.
What precautions must be taken while taking antibiotics ?
Answer:
Antibiotics should be taken after consulting a doctor. The complete dose of the antibiotics should be taken as prescribed. They should not be taken unnecessarly because they will kill the useful bacteria.
Question 5.
1. Write the causal organism of cholera.
2. Write any two symptoms of this disease.
3. Why ORS should be given to the patients suffering from cholera ? [MSE (iChandigarh) 2007]
Answer:
1. Cholera is caused by Vibrio cholerae.
2. Two symptoms of cholera are :
· profuse and painless watery diarrhoea.
· muscular cramps.
3. ORS should be given to the patients suffering from cholera to avoid excessive loss of body fluids.
Question 6.
Why are viruses considered to be on the borderline between living organisms and non-living things ? [DAV2007]
Answer:
Viruses cannot reproduce, respond to changes or use energy to grow. Since viruses reproduce in the host cell, scientist regard viruses as a link between living and non-living.
Question 7.
How are bacteria beneficial for us ? [NCT 2006]
Answer:
Bacteria are useful to us as :
· Nitrogen fixing bacteria increase the fertility of the soil.
· They can be used to form curd, alcohol, etc.
· They can decompose organic matter.
Question 8.
Write three types of bacteria on the basis of their shape. Give one example of each. [MSE (Chandigarh) 2005]
Answer:
Three types of bacteria are :
1. Bacillus or rod-shaped, e.g., Lactobacillus.
2. Coccus or spherical, e.g., Streptococcus.
3. Spirillum or spiral, e.g., Vibrio.
Question 9.
(a) Are bacteria plants or animals ? Give reasons in support of your answer.
(b) Write two differences between autotrophic and heterotrophic bacteria. [DAV2005]
Answer:
(a) Bacteria is considered as plant due to the presence of a rigid cell wall in it.
(b)
Autotrophic bacteria | Heterotrophic bacteria |
(i) Chlorophyll is present. | (i) Chlorophyll is absent. |
Question 10.
How does a housefly transmit diseases ? [MSE (Chandigarh) 1999]
Answer:
A housefly gets attracted towards garbage and excreta. The harmful microorganisms present in excreta and garbage easily stick to its fine array of body hair and are thus, transferred to food stuffs whenever they sit on them and a result food gets poisoned.
Question 11.
1. What are antibiotics ?
2. How are antibiotics manufactured ?
3. Name two important antibiotics.
Answer:
1. Medicines which kill or stop the growth of the disease causing microorganisms are called antibiotics.
2. The antibiotics are manufactured by growing specific microorganisms.
3. Two important antibiotics are Tetracycline and Bacitracin.
Question 12.
What will happen if you take antibiotics when not needed ?
Answer:
If you take antibiotics when not needed, you help bacteria in your body to develop resistance to them. Next time when you fall ill and need these antibiotics, they would be less effective.
Question 13.
How does a vaccine act ?
Answer:
The vaccine acts by making the body’s immune system to produce antibodies against the disease-causing microbe in the vaccine. The antibodies attack and destroy the weakened microbe as it enters the body.
Question 14.
How is common cold spread ?
Answer:
When a person suffering from common cold sneezes, fine droplets of moisture carrying thousands of viruses causing common cold are spread in the air. The viruses may enter the body of a healthy person while breathing.
Question 15.
How can you prevent the spread of communicable diseases ?
Answer:
It is better to avoid contact with the infected person. We should keep distance from infected persons.
Question 16.
Give the methods of prevention of cholera.
Answer:
Cholera can be prevented by :
· Vaccination.
· Maintaining good personal hygiene.
· Consuming properly cooked food and drinking boiled water.
Question 17.
How does food become ‘poison’ ?
Answer:
Microorganisms that grow on our food sometimes produce toxic substances. These make the food poisonous causing serious illness and even death.
Question 18.
What will happen if yeast powder is put in sugar solution and kept for few hours ? Name the process.
Answer:
When yeast powder is put in sugar solution and kept for few hours, fermentation takes place. The sugar is converted into alcohol by yeast and this process is known as Fermentation.
Ch:3 Synthetic Fibers and Plastics
Question 1.
Explain why some fibres are called synthetic.
Answer:
Some fibres are called synthetic fibres because they are made by man using chemicals.
Question 2.
Mark (✓) the correct answer.
Rayon is different from synthetic fibres because
(a) it has a silk-like appearance.
(b) it is obtained from wood pulp.
(c) its fibres can also be woven like those of natural fibres.
Answer:
(b) it is obtained from wood pulp.
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
(a) Synthetic fibres are also called ____ or ____ fibres.
(b) Synthetic fibres are synthesised from a raw material called _____
(c) Like synthetic fibres, plastic is also a _____
Answer:
(a) man-made, artificial fibres
(b) petrochemicals
(c) polymer
Question 4.
Give examples which indicate that nylon fibres are very strong.
Answer:
The following examples indicate that nylon fibres are very strong.
(i) They are used for making parachutes and ropes for rock climbing.
(ii) They are used in making seat-belts, fishing nets, tyre cord, a string for sports rackets and musical instruments.
Question 5.
Explain why plastic containers are favoured for storing food.
Answer:
Plastic containers are favoured for storing food because of the following reasons:
(i) the plastics do not react with the food stored in them.
(ii) the plastics are lightweight and are strong.
(iii) they are easy to handle and safe.
Question 6.
Explain the difference between thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics.
Answer:
| Thermoplastics | Thermosetting plastics |
| (i) These plastics softened on heating and can be bent easily. | (i) These plastics when moulded once, can’t be softened again. |
| (ii) They do not lose their plasticity. | (ii) They lose their plasticity. |
| (iii) Examples are polyethene, PVC, etc. | (iii) Examples are bakelite and melamine. |
Question 7.
Explain why the following are made of thermosetting plastics.
(a) Saucepan handles
(b) Electric plugs/switches/plugboards
Answer:
(a) Since, thermosetting plastics are a bad conductor of heat and do not get heated up while cooking, they are used for making saucepan handles.
(b) Since thermosetting plastics are a bad conductor of electricity and the electric current does not pass through such plastics, they are used for making electric plugs/switches/plugboards.
Question 8.
Categorise the materials of the following products into ‘can be recycled’ and ‘can not be recycled’.
Telephone instruments, plastic toys, cooker handles, carry bags, ballpoint pens, plastic bowls, plastic covering on electrical wires, plastic chairs, electrical switches.
Answer:
| Can be recycled | Cannot be recycled |
| Plastic toys carry bags, plastic bowls, plastic covering on electrical wires, plastic chairs. | Telephone instruments, cooker handles, ballpoint pens, electrical switches. |
Question 9.
Rana wants to buy shirts for summer. Should he buy cotton shirts or shirts made from synthetic material? Advise Rana, giving your reason.
Answer:
He should buy cotton shirts. This is because cotton has more capacity to hold moisture than synthetic clothes. In summers we have extensive sweating which is easily soaked by cotton shirts and hence, cotton clothes are much better than the clothes made from synthetic material.
Question 10.
Give examples to show that plastics are non-corrosive in nature.
Answer:
The literal meaning of non-corrosive is resistant to get destroyed by chemical action.
Following are the examples that show that plastics are non-corrosive in nature.
- Plastic containers do not react with items stored in it.
- They do not get rusted when exposed to moisture and air.
- They do not decompose when left in open for a long period.
Question 11.
Should the handle and bristles of a toothbrush be made of the same material? Explain your answer.
Answer:
No, the handle and bristles of a toothbrush should not be made of the same material. This is because our gums are soft and the bristles should be made of soft material so that it does not harm the gums. On the other hand, the handles should be made up of hard material so that it can give a firm grip.
Question 12.
‘Avoid plastics as far as possible’. Comment on this advice.
Answer:
Plastics must be avoided as far as possible. The materials made of plastics are non-biodegradable. The use of plastics has a bad effect on the environment. When the plastics are burnt, it releases a lot of poisonous fumes into the atmosphere causing air pollution. These plastic materials when eat up by the animals (like cows), choke their respiratory system. This can cause death of these animals. The waste plastic articles thrown here and there carelessly get into dirty water drains and sewers, and block them. In a nutshell, plastics can be considered a threat to our environment.
Question 13.
Match, the terms of column A correctly with the phrases given in column B.
| A | B |
| (i) Polyester | Prepared by using wood pulp |
| (ii) Teflon | Used for making parachutes and stockings |
| (iii) Rayon | Used to make non-stick cookware |
| (iv) Nylon | Fabrics do not wrinkle easily |
Answer:
(i) (d)
(ii) (c)
(iii) (a)
(iv) (b)
Question 14.
‘Manufacturing synthetic fibres is actually helping the conservation of forests’. Comment.
Answer:
In the manufacturing of synthetic fibres, we use only chemical substances and no natural materials, thus, in turn, we conserve forests.
Question 15.
Describe an activity to show that thermoplastic is a poor conductor of electricity.
Answer:
Arrange a circuit as shown in the given figure. Leave a gap between two ends of the wire. Place a ther-moplastic in the gap. Observe the bulb.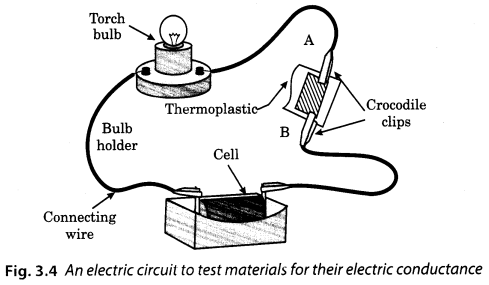
It is observed that the bulb does not glow. This shows that thermoplastic is a poor conductor of electricity.
Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Class 8 Science NCERT Intext Activities Solved
Activity 1 (NCERT Textbook, Page 34)
Take an iron stand with a clamp. Take a cotton thread of about 60 cm length. Tie it to the clamp so that it hangs freely from it as shown in Fig. 3.3.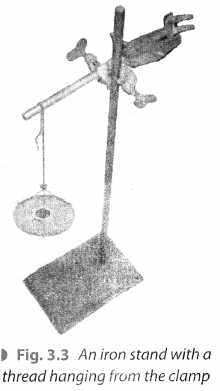
At the free end suspend a pan so that weight can be placed in it. Add weight one by one till the thread breaks. Note down the total weight required to break the thread. This weight indicates the strength of the fibre. Repeat the same activity with threads of wool, polyester, silk and nylon. Tabulate the data as shown in Table 3.1. Arrange the threads in order of their increasing strength.
Observation Table 3.1
| S. No. | Type of Thread/ Fibre | Total Weight required to break the thread |
| 1. | Cotton | 12 gm |
| 2. | Wool | 70 gm |
| 3. | Silk | 50 gm |
| 4. | Nylon | 100 gm |
(Precaution: Note that all threads should be of the same length and most of the same thickness.)
Activity 2 (NCERT Textbook, Page 36)
Take two cloth pieces of the same size, roughly half a metre square each. One of these should be from natural fibre. The other could be a synthetic fibre. You can take the help of your parents in selecting these pieces. Soak the pieces in different mugs each containing the same amount of water. Take the pieces out of the containers after five minutes and spread them in the sun for a few minutes. Compare the volume of the water remaining in each container.
Solution:
It is observed that the volume of water of the container in which natural fibre is soaked contains less water as compared to the container in which synthetic fibre is soaked. Thus, natural fibre absorbs more water as compared to synthetic fibre. When both the fibres were spread in the sun, it was observed that synthetic fibre took less time to dry than natural fibre.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 – 1 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain why some fibres are called synthetic. [NCERT]
Answer:
Some fibres are called synthetic because they are made by human beings.
Question 2.
Mark the correct answer.
Rayon is different from synthetic fibres because [NCERT]
- It has a silk-like appearance.
- It is obtained from wood pulp.
- Its fibres can also be woven like those of natural fibres.
Answer:
- It is obtained from wood pulp.
Question 3.
Give examples which indicate that nylon fibres are very strong.
Answer:
Parachutes and nylon ropes are used for rock climbing.
Question 4.
Name the plastic whose sheets are used for packing liquids.
Answer:
Polythene.
Question 5.
Why is teflon used as tape for sealing purpose ?
Answer:
Becausee of its toughness, teflon is used as tape for sealing purpose.
Question 6.
Name the first fully synthetic fibre.
Answer:
Nylon.
Question 7.
Why nylon is used for making parachutes ?
Answer:
Nylon is used for making parachutes, because it is very strong, elastic and light.
Question 8.
Name the material used for making ropes for rock climbing.
Answer:
Nylon.
Question 9.
What is polyester ?
Answer:
Polyester is made up of the repeating units of an ester.
Question 10.
Name the plastic used for making polythene bags.
Answer:
Polythene bag is made of plastic which is a polymer of ethene.
Question 11.
What name is given to plastics which can be re-set a number of times ?
Answer:
Thermoplastics.
Question 12.
Classify the following into thermosetting and thermoplastics-combs, bakelite, melamine, toys.
Answer:
Thermosetting – bakelite, melamine
Thermoplastics – combs, toys
Question 13.
Why are the chemicals in the laboratory stored in plastic containers ?
Answer:
Plastics are non-reactive, so they can be used for storing chemicals.
Question 14.
Can you store pickles in plastic containers ? Why ?
Answer:
Plastics are non-reactive, so pickles can be stored in them.
Question 15.
Why are the electric wires covered with plastic ?
Answer:
Plastic is a poor conductor of electricity, therefore, the wires are covered with it.
Question 16.
Why do we use plastic cookwares in microwave ovens ?
Answer:
We use plastic cookware in microwave ovens, because they are not affected by heat but the food is cooked.
Question 17.
Tin takes about 100 years to degenerate. Is it biodegradable or non-biodegradable ?
Answer:
Tin is non-biodegradable.
Question 18.
Is it advisable to use recycled plastic containers for storing food ?
Answer:
No, we should not use recycled plastic containers for storing food because they contain colouring agents.
Question 19.
As a responsible citizen, what are the 4R’s we should remember ?
Answer:
Reduce, Reuse, Recycle and Recover.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 – 2 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Aperson has to make a non-stick pan. He has three types of plastic-Bakelite, Teflon and PVC. Which plastic will he use for coating and why ?
Answer:
The person will use Teflon because it is not affected by heat and does not react chemically with other substances.
Question 2.
Explain the difference between thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics. [NCERT]
Answer:
| Thermosetting | Thermoplastic |
| (i) These plastics can be moulded and (ii) e.g.,Bakelite and melamine. | (i) These plastics can be moulded and reset a number of times. (ii) e.g. Polythene and PVC. |
Question 3.
Differentiate between natural and synthetic fibres.
Answer:
Natural fibres are obtained from nature, e.g., cotton whereas synthetic fibres are made by man, e.g., nylon.
Question 4.
How is rayon made ? Give one advantage of using rayon.
Answer:
Rayon is obtained from wood pulp by treating it chemically. It is cheaper than silk, but can be woven like silk fibre.
Question 5.
Is nylon fibre so strong, that we can use it to make parachutes ?
Answer:
Yes, nylon is very strong and it can be used for making parachutes.
Question 6.
Give some uses of PET.
Answer:
PET is used for making bottles, utensils, fibres and wires.
Question 7.
Give the composition of Polycot and Polywool.
Answer:
Polycot is a mixture of polyester and cotton, Poly wool is a mixture of polyester and wool.
Question 8.
What properties of plastics make it useful for many things ?
Answer:
Plastics can be recycled, reused, coloured, melted, rolled into sheets or made into wires, so they are very useful.
Question 9.
Why is melamine used for making kitchenware ?
Answer:
Melamine resists fire and can tolerate heat better than other plastics. So, it is used for making kitchenware.
Question 10.
Buckets made up of plastics are better. Why ?
Answer:
Buckets made up of plastic are better because they are light, strong and durable.
Question 11.
Differentiate between biodegradable and non-biodegradable materials.
Answer:
| Biodegradable Materials | Non-biodegradable Materials |
| (i) A meterial which gets decomposed through natural processes, such as action of bacteria. (ii) e.g., cotton or jute. | (i) A material which does not get decomposed by natural processes. (ii) e.g., plastics. |
Question 12.
Should the handle and bristles of a tooth brush be made of the same material ? Explain your answer. [NCERT]
Answer:
No, the handle and bristles of tooth brush cannot be made of the same plastic. The handle is hard but the bristles are soft and flexible.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 – 3 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Give three advantages of polythene over natural materials. [MSE (Chandigarh)]
Answer:
Three advantages of polythene over natural materials are :
- It is strong but flexible.
- Can be rolled into sheets.
- Water resistant.
Question 2.
Give one use each of bakelite, nylon and acrylic.
Answer:
Bakelite is used for making plugs and switches. Nylon is used in textile industry to produce clothes. Acrylic is used as a substitute of natural wool for knitting sweaters, blankets etc.
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words. [NCERT]
- Synthetic fibres are also called ……….. or ……….
- Synthetic fibres are synthesised from raw material called …………
- Like synthetic fibres, plastic is also a …………..
Answer:
- artificial, man-made
- mono or petrochemicals
- polymers.
Question 4.
Explain why plastic containers are favoured for storing food. [NCERT]
Answer:
Food can be stored in plastic containers because
- Plastics are non-reactive.
- Plastics are light and strong.
- Plastics are durable.
Question 5.
Explain why the following are made of thermosetting plastics : [NCERT]
- Saucepan handles
- Electric plugs/switches/plug boards.
Answer:
- Saucepan handles are made of thermosetting plastics because they are bad conductors of heat.
- Electric plugs/switches/plug boards are made of thermosetting plastics because they are bad conductors of electricity.
Question 6.
Rana wants to buy shirts for summer. Should he buy cotton shirts or shirts made from synthetic material ? Advice Rana, giving your reason.
Answer:
Rana should buy cotton shirts. Cotton clothes are preferred in summer because they absorb sweat and the person feels cool whereas synthetic materials do not absorb sweat and the person feels uncomfortable.
Question 7.
Give examples to show that plastics are noncorrosive in nature. [NCERT]
Answer:
- Buckets made of iron get rusted but those made of plastic are not rusted.
- Food can be stored in plastic containers, as they are resistant to chemicals in the food
- Teflon coated pans are used instead of metallic as it doesnot react with chemicals in the food.
Question 8.
Give three advantages of rayon.
Answer:
Advantages of rayon are :
- It is cheap.
- It can be dyed in many colours.
- It can be woven like silk.
Question 9.
What are the advantages of nylon ?
Answer:
Nylon fibre is strong, elastic and light. It is lustrous and easy to wash.
Question 10.
Give some uses of nylon.
Answer:
Nylon can be used for making socks, ropes, tents, toothbrushes, sleeping bags, curtains, parachutes and ropes for rock climbing.
Question 11.
What are the advantages of using fabrics made of polyester ?
Answer:
Fabrics made of polyester
- do not get wrinkled easily
- are easy to wash,
- easy to maintain.
Question 12.
Why people prefer to wear acrylic sweaters than pure wool sweaters ?
Answer:
Acrylic sweaters are cheaper and easy to maintain. They are available in many colours.
Question 13.
What are the disadvantages of wearing synthetic fabrics ?
Answer:
Synthetic fabric catches fire very easily. It melts and sticks to the body of the person wearing it. During summers, synthetic fibres do not absorb sweat and a person wearing it feels uncomfortable.
Question 14.
Give the characteristics of synthetic fibres.
Answer:
Synthetic fibres dry up soon, are durable, less expensive, readily available and easy to maintain.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 – 5 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Categorise the materials of the following products into ‘can be recycled’ and ‘cannot be recycled’. [NCERT]
Telephone instruments, plastic toys, cooker handles, carry bags, ball point pens, plastic bowls, plastic covering on electrical wires, plastic chairs, electrical switches.
Answer:
| Can be recycled | Non-biodegradable Materials |
| Toys, carry bags, plastic bowls, plastic covering on electrical wires, plastic chairs. | Telephone instruments, cooker handles, electric switches, ball point pens, electrical switches. |
Question 2.
Match the terms of Column A correctly with the phrases given in Column B. [NCERT]
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Polyester (b) Teflon (c) Rayon (d) Nylon | (i) Prepared by using wood pulp. (ii)Used for making parachutes and stockings. (iii) Used to make non-stick cookwares. (v) Fabrics do not wrinkle easily. |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Polyester | (iv) Fabrics do not wrinkle easily. |
| (b) Teflon | (iii) Used to make non-stick cookwares. |
| (c) Rayon | (i) Prepared by using wood pulp. |
| (d) Nylon | (ii) Used for making parachutes and stockings. |
Question 3.
‘Manufacturing synthetic fibres is actually helping conservation of forests’. Comment. [NCERT]
Answer:
The said statement is correct to a certain extent. The forests would be conserved if synthetic fibres are used, but other effects of synthetic fibres are more harmful. Disposal of synthetic fibres causes lot of environmental pollution. When synthetic fibres bum, lot of smoke is produced.
Question 4.
‘Avoid plastics as far as possible’. Comment on this advice. [NCERT]
Answer:
Plastics are very useful, but it causes serious environmental and health concern :
- Plastics are non-biodegradable.
- Careless disposal of plastic bags, chokes, drains and blocks the soil.
- If eaten by cows, it can kill them.
- Plastic bags can also contaminate foodstuffs due to poisonous dyes getting absorbed into food
Question 5.
How is plastic useful in healthcare industry ?
Answer:
In healthcare, plastics are used
- for packaging of tablets
- as threads for stitching wounds
- in syringes
- doctor gloves
- for making a number of medical instruments.
Question 6.
“Even though plastics are very useful, they are not environment friendly.” Justify the statement.
Answer:
Plastics are very useful, but their disposal is a big problem. Plastics are non-biodegradable and take many years to decompose. They release a lot of poisonous fumes, when burnt so they cause environmental pollution.
Question 7.
Give methods by which pollution due to plastics can be solved.
Answer:
Pollution due to plastics can be solved by following methods :
- Avoid the use of plastics as far as possible.
- Use bags, made of jute or cloth.
- Biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes should be separated and disposed off separately.
- Plastics should be recycled and reused.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 MCQs
Question 1.
Electrical switches are made of
(a) nylon
(b) bakelite
(c) polythene
(d) melamine
Answer:
(b)
Question 2.
Out of the following, which is not biodegradable ?
(a) Vegetable peels
(b) Plastic bags
(c) Cotton
(d) Jute
Answer:
(b)
Question 3.
Clothes made of which fabric are best suited for hot climate ?
(a) Cotton
(b) Nylon
(c) Acrylic
(d) Polycot
Answer:
(a)
Question 4.
Out of the following, which is not a natural fibre ?
(a) Cotton
(b) Silk
(c) Jute
(d) Rayon
Answer:
(d)
Question 5.
Naturally occurring po/ymer is
(a) cellulose
(b) polyester
(c) nylon
(d) PVC
Answer:
(a)
Question 6.
Plastic used for coating non-stick pans is
(a) PVC
(b) ester
(c) bakelite
(d) melamine
Answer:
(d)
Question 7.
Pickles are kept in plastic containers because plastic containers are
(a) non-corrosive
(b) light
(c) colourful
(d) cheap
Answer:
(a)
Question 8.
Which of the following is a thermoplastic
(a) Bakelite
(b) Melamine
(c) Polythene
(d) Jute
Answer:
(c)
Question 9.
Which of the following can be recycled?
(a) Plastic bowls
(b) Ballpoint pens
(c) Telephone instruments
(d) Electrical switches
Answer:
(a)
Question 10.
Which material is best suited for covering electric wires?
(a) Plastic bowls
(b) PVC
(c) Polystyrene
(d) Nylon
Answer:
(b)
Question 1.
Which of the following can be beaten into thin sheets?
(a) Zinc
(b) Phosphorus
(c) Sulphur
(d) Oxygen
Answer:
(a) Zinc
Question 2.
Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) All metals are ductile.
(b) All non-metals are ductile.
(c) Generally, metals are ductile.
(d) Some non-metals are ductile.
Answer:
(c) Generally, metals are ductile
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks.
(a) Phosphorus is a very ____ non-metal.
(b) Metals are _____ conductors of heat and _____
(c) Iron is ______ reactive than copper.
(d) Metals react with acids to produce ______ gas.
Answer:
(a) reactive
(b) good, electricity
(c) more
(d) hydrogen
Question 4.
Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false.
(a) Generally, non-metals react with acids.
(b) Sodium is a very reactive metal.
(c) Copper displaces zinc from zinc sulphate solution.
(d) Coal can be drawn into wires.
Answer:
(a) False
(b) True
(c) False
(d) False
Question 5.
Some properties are listed in the following Table. Distinguish between metals and non-metals on the basis of these properties.
| Properties | Metals | Non-metals |
| 1. Appearance | ||
| 2. Hardness | ||
| 3. Malleability | ||
| 4. Ductility | ||
| 5. Heat Conduction | ||
| 6. Conduction of Electricity |
Answer:
| Properties | Metals | Non-metals |
| 1. Appearance | have metallic lustre | dull |
| 2. Hardness | hard | soft |
| 3. Malleability | malleable | non-malleable |
| 4. Ductility | ductile | non-ductile |
| 5. Heat Conduction | good conductors | bad conductors |
| 6. Conduction of Electricity | good conductors | bad conductors/insulators |
Question 6.
Give reasons for the following.
(a) Aluminium foils are used to wrap food items.
(b) Immersion rods for heating liquids are made up of metallic substances.
(c) Copper cannot displace zinc from its salt solution.
(d) Sodium and potassium are stored in kerosene.
Answer:
(a) Aluminium is highly malleable and it can be easily beaten in sheets to make its foil for wrapping purposes. It is also soft and does not react with food items. That is why aluminium foils are used . to wrap food items.
(b) Immersion rods made up of metallic substances because metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. They get hot very soon on the passage of electric current and warm the water.
(c) Copper is less reactive than zinc. So it cannot displace zinc from its solution.
(d) Sodium and potassium are highly reactive, so they are stored in kerosene.
Question 7.
Can you store the lemon pickle in an aluminium utensil? Explain.
Answer:
No, we cannot store lemon pickle in an aluminium utensil because aluminium is a metal and metals readily react with acids to produce hydrogen. When aluminium comes in contact with lemon, which is acidic, would react to give hydrogen and the pickles will be spoiled.
Question 8.
Match the substances given in column A with their uses given in column B.
| A | B |
| Gold | Thermometers |
| Iron | Electric wire |
| Aluminium | Wrapping food |
| Carbon | Jewellery |
| Copper | Machinery |
| Mercury | Fuel |
Answer:
(i) (d)
(ii) (e)
(iii) (c)
(iv) (f)
(v) (b)
(vi) (a)
Question 9.
What happens when
(a) Dilute sulphuric acid is poured on a copper plate?
(b) Iron nails are placed in a copper sulphate solution?
Write word equations of the reactions involved.
Answer:
(a) No reaction will take place because copper is very less reactive.
(b) Iron being more reactive than copper will replace copper from its solution and brown coating of copper is deposited on the iron nails. Also, the blue colour turns green.
Iron + Copper sulphate (solution) → Iron sulphate (solution) + Copper
Question 10.
Saloni took a piece of burning charcoal and collected the gas evolved in a test tube.
(a) How will she find the nature of the gas?
(b) Write down the word equations of all the reactions taking place in this process.
(a) She can find the nature of the gas by using a wet litmus paper. After bringing the litmus paper in contact with the gas, if it turns the blue litmus paper into red, it is acidic. Similarly, if it turn the red litmus into blue, it is basic.
(b) (i) Carbon + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide
(ii) Carbon dioxide + Lime water → Milky
Question 11.
One day Reeta went to a jeweller’s shop with her mother. Her mother gave an old gold jewellery to the goldsmith to polish. Next day when they brought the jewellery back, they found that there was a slight loss in its weight. Can you suggest a reason for the loss in weight?
Answer:
The gold jewellery is dipped into an acidic solution called aqua regia (a mixture of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid) for polishing. On dipping the gold jewellery in the acid solution, the outer layer of gold dissolves and the inner shiny layer appears. This causes a slight loss in its weight.
Materials: Metals and Non-Metals Class 8 Science NCERT Intext Activities Solved
Activity 1 (NCERT Textbook, Page 44)
Take a small iron nail, a coal piece, a piece of thick aluminium wire and a pencil lead. Beat the iron nail with a hammer (Fig. 4.1).
(But take care that you don’t hurt yourself in the process). Try to hit hard. Hit hard the aluminium wire also. Then repeat the same kind of treatment on the coal piece and pencil lead. Record your observations in Table 4.1.
Table 4.1 Malleability of Materials
| Object/Material | Change in Shape (Flattens/Breaks into Pieces) |
| Iron nail | Flattens |
| Coal piece | Breaks into pieces |
| Aluminium wire | Flattens |
| Pencil lead | Breaks into pieces |
Solution: This activity shows that iron and aluminium are malleable while coal piece and pencil lead are brittle. Thus, metals are malleable and non-metals are non-malleable.
Activity 2 (NCERTTextbook, Page 45)
Recall how to make an electric circuit to test whether electricity can pass through an object or not (Fig. 4.2).
You might have performed the activity with various objects in Class VI. Now, repeat the activity with the materials mentioned in Table 4.2. Observe and group these materials into good conductors and poor conductors.
| S. No. | Materials | Good Conductor/Poor Conductor |
| 1. | Iron rod/nail | Good conductor |
| 2. | Sulphur | Poor conductor |
| 3. | Coal piece | Poor conductor |
| 4. | Copper wire | Good conductor |
Solution:
It shows that metals are good conductors of electricity and non-metals are poor conductors of electricity.
Activity 3 (NCERT Textbook, Page 46)
Let us check the nature of rust formed as a result of the reaction between iron, oxygen and water. Collect a spoonful of rust and dissolve it in a very little amount of water. You will find that the rust remains suspended in water. Shake the suspension well. Test the solution with red and blue litmus papers (Fig. 4.3).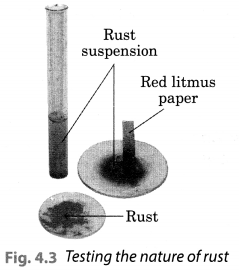
What do you observe? Is the solution acidic or basic?
Solution:
We observed that the red litmus paper turns blue which shows that the nqjure of rust is basic. Blue litmus paper do not show any colour change with the solution.
Activity 4 (NCERT Textbook, Page 47)
(To be demonstrated by the teacher in the class)
Take a small amount of powdered sulphur in a deflagrating spoon and heat it. If deflagrating spoon is not available, you may take a metallic cap of any bottle and wrap a metallic wire around it and give it the shape shown in Fig. 4.4 (a).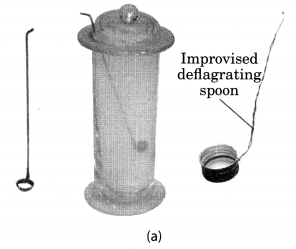
As soon as sulphur starts burning, introduce the spoon into a gas jar/glass tumbler [Fig. 4.4(a)]. Cover the tumbler with a lid to ensure that the gas produced does not escape. Remove the spoon after some time. Add a small quantity of water into the tumbler and quickly replace the lid. Shake the tumbler well. Check the solution with red and blue litmus papers [Fig. 4.4. (b)].
Solution:
We observed that the solution of oxide turns the blue litmus red which shows that the solution is acidic in nature. This also shows that oxide of non-metals is acidic in nature.
Activity 5 (NCERT Textbook, Page 48)
Take a 250 mL beaker/glass tumbler. Fill half of it with water. Now carefully cut a small piece of sodium metal. Dry it using filter paper and wrap it in a small piece of cotton. Put the sodium piece wrapped in cotton into the beaker. Observe carefully.
When reaction stops, touch the beaker. What do you feel? Has the beaker become hot? Test the solution with red and blue litmus papers. Is the solution acidic or basic?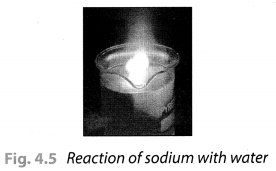
Solution:
On touching the beaker, it was felt hot. The solution turns the red litmus paper to blue which shows it is basic in nature. Blue litmus paper do not show any colour change with the solution.
Activity 6 (NCERT Textbook, Page 49)
Take samples of metals and non-metals given in Table 4.3 in separate test tubes and label them as A, B, C, D, E and F. With the help of a dropper add 5 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid to each test tube one by one. Observe the reactions carefully. If no reaction occurs in the cold solution, warm the test tube gently. Bring a burning matchstick near the mouth of each test tube.
Repeat the same activity using dilute sulphuric acid instead of dilute hydrochloric acid. Record your observations in Table 4.3.
Solution:
This activity shows that metals usually displace hydrogen from dilute acids whereas non-metals do not do so and no hydrogen gas is evolved.
Activity 7 (NCERT Textbook, Page 50)
Prepare a fresh solution of sodium hydroxide in a test tube by dissolving 3-4 pellets of it in 5 mL of water. Drop a piece of aluminium foil into it. Bring a burning matchstick near the mouth of the test tube. Observe carefully.
Solution:
We observed that a colourless gas is evolved which burns with a pop sound. This shows that aluminium react with bases on heating to produce hydrogen gas.
Activity 8 (NCERT Textbook, Page 50)
Take five 100 mL beakers and label them A, B, C, D and E. Take about 50 mL of water in each beaker. Dissolve in each beaker a teaspoonful of each substance as indicated in Fig. 4.6 (a), (i) Keep the beakers undisturbed for some time, (ii) Record you observations in your notebook.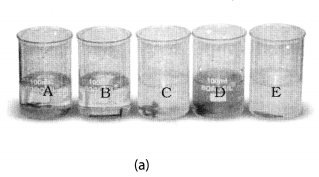
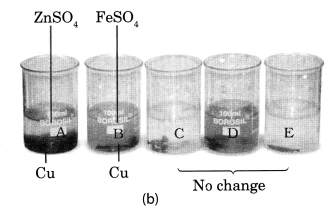
Beaker A: Copper sulphate (CuSO4) + Zinc granule (Zn), Beaker B: Copper sulphate (CuSO4) + Iron nail (Fe)
Beaker C: Zinc sulphate (ZnSO4) + Copper turnings (Cu), Beaker D: Iron sulphate (FeSO4) + Copper turnings (Cu)
Beaker E: Zinc sulphate (ZnSO4) + Iron nail (Fe)
Solution:
In beaker ‘A’ zinc (Zn) replaces copper (Cu) from copper sulphate (CuS04) solution. That is why the blue colour of copper sulphate changes to colourless and a powdery red mass of copper is deposited at the bottom of the beaker. The reaction can be represented as follows: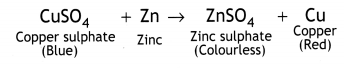
In beaker B, iron replaces copper from its solution. That is why the blue colour of copper sulphate changes to green colour of ferrous sulphate.
In beaker C, D and E no change in colour or heat evolution is observed. This indicates that the metals are unable to displace the other metals from its solution.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 – 1 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Non-metals cannot be drawn into wires. Why ? [DAV2008]
Answer:
Non-metals are not ductile, therefore they cannot be drawn into wires.
Question 2.
Complete the following equation :
Zn + 2HCl ——-> __+ __ [MSE (Chandigarh) 2007]
Answer:
Zn + 2HCl ——-> ZnCl2 + H2
Question 3.
Which of the following can be beaten into thin sheets ? [NCERT]
- Zinc
- Phosphorus
- Sulphur
- Oxygen.
Answer:
Zinc.
Question 4.
The number of metals is much ………….. than non-metals.
Answer:
More.
Question 5.
……… are the good conductors of heat and electricity.
Answer:
Metals.
Question 6.
Examples of metals are ………., ……. and ………
Answer:
Iron, sodium and nickel.
Question 7.
Examples of non-metals are ………. , …….. and …….
Answer:
Sulphur, chlorine and oxygen.
Question 8.
Explain the term ‘metallurgy’.
Answer:
Metallurgy is the science of extracting metals from their ores and purifying them for various uses.
Question 9.
State general steps involved in metallurgy of a metal.
Answer:
The general steps of metallurgy are :
- Concentration of ore.
- Reduction of the metal compound.
- Refining of metal.
Question 10.
Metals are (softer/harder) than non-metals.
Answer:
Harder.
Question 11.
Most non-metals are (bad/good) conductors of heat.
Answer:
Bad.
Question 12.
The property that allows the metals to be hammered into thin sheets is called (ductility/ malleability).
Answer:
Malleability.
Question 13.
Melting point of most non-metals is (higher/lower) than metals.
Answer:
Lower.
Question 14.
(Metals/non-metals) display lustre.
Answer:
Metals.
Question 15.
Arrange the following metals in the order of their decreasing chemical activity : magnesium, potassium, iron, gold.
Answer:
Potassium, magnesium, iron, gold.
Question 16.
Can copper displace iron from iron sulphate solution ? Give reasons.
Answer:
Copper cannot displace iron from iron sulphate because copper is less reactive than iron.
Question 17.
(Platinum/iron) is the member of the family of noble metals.
Answer:
Platinum.
Question 18.
Pure gold is (24/100) carats.
Answer:
24.
Question 19.
International standards of weights are made of (gold-silver/platinum-iridium) alloy.
Answer:
Platinum-iridium.
Question 20.
Gold dissolves in (aqua regia/aqueous solution of silver nitrate).
Answer:
Aqua regia.
Question 21.
Silver tarnishes due to (nitrogen oxides/hydrogen sulphide) in the air.
Answer:
Hydrogen sulphide.
Question 22.
Why is aluminium used in making aeroplanes ?
Answer:
Aluminium is used in making aeroplanes, as it is light and has high resistance to corrosion when exposed to air which aircrafts demand the most.
Question 23.
What type of oxides are formed by metals ?
Answer:
Metals form basic oxides.
Question 24.
What type of oxides are formed by non-metals ?
Answer:
Non-metals form acidic or neutral oxides.
Question 25.
How does phosphorus occur in nature ?
Answer:
Phosphorus occurs in nature in the combined state as it has strong affinity for oxygen.
Question 26.
Give the different forms of silica in nature.
Answer:
Silica occurs in nature as ordinary sand, flint, quartz and opal.
Question 27.
Which metal foil is used in packing of some medicine tablets ?
Answer:
Aluminium.
Question 28.
Name the soft metal which can be cut with a knife.
Answer:
Sodium or potassium.
Question 29.
Name the non-metal used in vulcanization.
Answer:
Sulphur.
Question 30.
Name one metal which is not malleable.
Answer:
Zinc or arsenic.
Question 31.
Name one non-metal which has lustre.
Answer:
Graphite or Iodine.
Question 32.
What would happen to iron railings if they are not painted ?
Answer:
They will get rusted.
Question 33.
Name the element commonly used for converting edible vegetable oils into vanaspati ghee.
Answer:
Hydrogen.
Question 34.
Name the element used for making containers of dry cells.
Answer:
Zinc.
Question 35.
Which metal is used for making radiators of cars ?
Answer:
Copper.
Question 36.
Name the metal whose salt is used for making photographic films.
Answer:
Silver.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 – 2 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
White phosphorous has to be kept in water. Why ? [NCT2007]
Answer:
Phosphorus is to be kept in water to prevent its contact with air because it is highly reactive.
Question 2.
Can you store lemon pickle in an aluminium utensils ? Explain. [NCERT]
Answer:
We cannot store acidic food stuffs in aluminium utensils because aluminium reacts with acids. The food gets spoilt.
Question 3.
One day Reeta went to a jeweller’s shop with her mother. Her mother gave an old gold jewellery to the goldsmith to polish. Next day when they brought the jewellery back, they found that there was a slight loss in its weight. Can you suggest a reason for the loss in weight ? [NCERT]
Answer:
The goldsmith must have used acid to clean the gold jewellery and some gold must have dissolved in it. Therefore, there was loss in weight of the jewellery.
Question 4.
Write short notes on
- Metallurgical processes
- Uses of common metals and non-metals
- Noble metals
Answer:
- Metallurgical process can be divided into following steps :
- Concentration of the ore
- Reduction of metal compound to get free metal
- Refining of metal.
- Uses of common metals and non-metals :
Uses of metals – for making machinery, automobiles, industrial gadgets, building, bridges, cooking utensils, electrical gadgets, jewellery, sheets.
Uses of non-metals – oxygen is used by plants and animals for their survival, nitrogen is used by plants for their growth, chlorine is used in water purification to kill germs, sulphur is used for making sulphuric acid, tincture iodine has antiseptic properties. - Noble metals – Gold, silver and platinum are noble metals. They occur free in nature . and maintain their lustre for a long time. Platinum, gold and silver are used for making jewellery as they do not tarnish.
Question 5.
Purity of gold is 15 carat. What is the percentage’of gold in the ornaments ?
Answer:
24 carat purity of gold =100
∴ 1 carat purity or gold = 100/24
15 carat purity of gold = (100*15)/24 = 62.5 %
Question 6.
Give two uses of sulphur in chemical industry.
Answer:
- It is used in the manufacture of sulphuric acid.
- It is used in the manufacture of carbon disulphide, which is used as an industrial solvent.
Question 7.
How is sulphur useful in agriculture ? How is sulphur useful in medicine ?
Answer:
Sulphur powder is an excellent insecticide and fungicide. It is used in spraying fruit trees.
- Sulphur is the main constituent of skin ointments.
- Metallic sulphides of sulphur are used in the preparation of Ayurvedic medicines.
Question 8.
Give two important uses of silver.
Answer:
- It is used for making coins.
- Silver salts (silver bromide and silver iodide) are used for making photographic films.
Question 9.
Give two uses of gold.
Answer:
- Gold is used for making ornaments.
- Gold foils are used in the preparation of Ayurvedic medicines.
Question 10.
Give two uses of platinum.
Answer:
- It is used as a catalyst in the manufacture of sulphuric and nitric acid.
- Platinum catalytic converters use platinum as catalytic agent.
Question 11.
Which of the following will form acidic oxide and why :
P, K, Na, Ca?
Answer:
P (Phosphorus) will form acidic oxide because it is a non-metal.
Question 12.
You are given two materials X and Y. On hammering X is flattened, but Y breaks. Which one is a metal ?
Answer:
X is a metal because it flattens, i.e., it is malleable.
Question 13.
There are four materials A, B, C and D. A and D are hard and shiny, but B and C are dull and not very hard. Identify the metals and non-metals from A, B, C and D.
Answer:
A and D are metals.
B and C are non-metals.
Question 14.
Gaurav knows that wires can be made from copper and aluminium. He tries to make wire . from sulphur and carbon. Will he succeed ? Give reason also.
Answer:
No, he will not succeed because sulphur and carbon are non-metals. Non-metals are not ductile, that is, they cannot be drawn into wires.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 – 3 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
- Identify the most reactive and least reactive metal amongst the followings :
Al, K, Cu, Au. - An iron knife kept dipped in blue copper sulphate solution changes to light green. Why ? Write the equation also. [KVS 2005]
Answer:
- Most reactive metal is K and least reactive metal is Au.
- An iron knife kept dipped in blue copper sulphate solution changes to light green because iron replaces copper from copper sulphate and forms iron sulphate. This happens because iron is more reactive than copper.
Fe + CuSO4 ——> FeSO4 + Cu
Question 2.
Give reasons, why :
- Silver is used in jewellery.
- Copper is used in electrical wiring.
- Sodium is stored in kerosene oil.
Answer:
- Silver does not corrode and it is malleable and ductile, therefore, it can be used in jewellery.
- Copper is used in electrical wiring because it is a good conductor of electricity.
- Sodium has low ignition temperature. It oxidises quickly and bums when exposed to air. It can only be stored in a liquid hydrocarbon like mineral oil or kerosene oil.
Question 3.
Taking examples of magnesium and sulphur explain how metals and non-metals produce oxides with different characteristics.
Answer:
Magnesium bums in oxygen to form magnesium oxide, which dissolves in water to form magnesium hydroxide – an alkali.
2Mg + O2 ——-> 2MgO
MgO + H2O ——-> Mg(OH)2
Magnesium hydroxide changes red litmus into blue.
Sulphur bums in air to form sulphur dioxide, which dissolves in water to form sulphurous acid – an acid which turns blue litmus into red.
S + O2 ——> SO2
SO2 + H2O ——–> H2SO3
Question 4.
Compare the following chemical properties of metals and non-metals.
- Formation of ions
- Action with dilute acids
- Action with hydrogen.
Answer:
- Formation of ions.
Metals form cations whereas non-metals form anions. - Action with dilute acids.
Metals react with dilute mineral acid to liberate hydrogen.
Non-metals do not react with dilute mineral acids. - Action with hydrogen.
Metals do not react with hydrogen but non-metals react with hydrogen to form hydrides.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 – 5 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What happens when [KVS 2008]
(a) Hydrochloric acid is poured on aluminium foils ?
(b) Sodium is placed in water ?
(c) Sulphur dioxide is dissolved in water ?
(Write the chemical equation of the reaction involved)
Answer: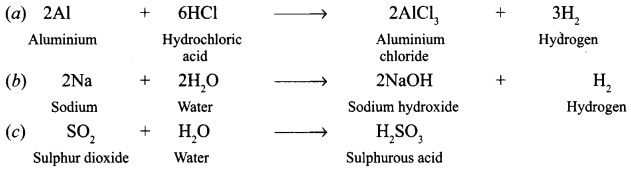
Question 2.
- A copper spoon had fallen into a container containing dil.HCl. What would happen to it in three days time ? [DAV2008]
- Give reasons for the following :
- Metals are used for making bells.
- We can’t use pure gold to make jewellery.
- A metal ribbon bums in air with bright white light and forms a white powder.
- Which metal is this ?
- Give the equation of the reaction taking place.
- The metallic oxide formed would be acidic or basic in nature ?
Answer:
- Nothing will happen as copper does not react with hydrochloric acid.
- Metals have the property of sonorosity so they are used for making bells.
- Pure gold cannot be used for making jewellery because it is very soft.
- Magnesium.
- 2Mg + O2 ——> 2MgO
- Basic in nature.
Question 3.
Give reasons for the following : [KVS 2007]
- Silver is used in making mirrors.
- Aluminium is used to make electrical wire.
- Iron is used in construction of bridges and houses.
- Graphite is used as an electrode in the dry cell.
- Iron sheets are galvanised before use.
Answer:
- Silver has the ability to reflect light, therefore, it is used for making mirrors.
- Aluminium is a good conductor of electricity, so, it is used for making electrical wires.
- Iron is a strong metal, therefore, it is mixed with concrete to make bridges and houses.
- Graphite is a good conductor of electricity, therefore, it is used as an electrode in dry cell.
- Iron sheets are galvanised before use so that they do not corrode.
Question 4.
Which of the following statements is correct ? [NCERT]
- All metals are ductile.
- All non-metals are ductile.
- Generally, metals are ductile.
- Some non-metals are ductile.
Answer:
Generally, metals are ductile.
Question 5.
Fill in the blanks : [NCERT]
- Phosphoms is a very ………… non-metal.
- Metals are …….. conductors of heat and ………
- Iron is ……… reactive than copper.
- Metals react with acids to produce ………. gas.
Answer:
- reactive
- good, electricity
- more
- hydrogen.
Question 6.
Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false. [NCERT]
- Generally, non-metals react with acids. ( )
- Sodium is a very reactive metal. ( )
- Copper displaces zinc from zinc sulphate solution. ( )
- Coal can be drawn into wires. ( )
Answer:
- F
- T
- F
- F
Question 7.
Some properties are listed in the following Table. Distinguish between metals and non-metals on the basis of these properties. [NCERT]
| Properties | Metals | Non-metals |
| 1. Appearance 2. Hardness 3. Malleability 4. Ductility 5. Heat conduction 6. Conduction of electricity |
Answer:
| Properties | Metals | Non-metals |
| 1. Appearance | Solid at room temperature except mercury. | They are either solids or gases except bromine (liquid). |
| 2. Hardness | They are hard | They are brittle. |
| 3. Malleability | Malleable | Non-malleable |
| 4. Ductility | Ductile | Non-ductile |
| 5. Heat conduction | Good conductors | Bad conductors |
| 6. Conduction of electricity | Good conductors | Bad conductors |
Question 8.
Give reasons for the following : [NCT 2010]
- Aluminium foils are used to wrap food items.
- Immersion rods for heating liquids are made up of metallic substances.
- Copper cannot displace zinc from its salt solution.
- Sodium and potassium are stored in kerosene.
Answer:
- Aluminium is a highly malleable metal and can be made into foils. So, it can be used to wrap food items.
- Metals are good conductors of electricity, therefore, they are used for making immersion rods.
- Copper is less reactive than zinc. Therefore, it cannot displace zinc from its salt solution.
- Sodium and potassium are highly reactive metals. On exposure to air, they get oxidized. To avoid this they are stored in kerosene.
Question 9.
Match the substances given in Column I with their uses given in Column II. [NCERT]
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Gold | (i) Thermometers |
| (b) Iron | (ii) Electric wire |
| (c) Aluminium | (iii) Wrapping food |
| (d) Carbon | (iv) Jewellery |
| (e) Copper | (v) Machinery |
| (f) Mercury | (vi) Fuel |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Gold (b) Iron (c) Aluminium (d) Carbon (e) Copper (f) Mercury | (iv) Jewellery (v) Machinery (iii) Wrapping food (vi) Fuel (ii) Electric wire (i) Thermometers |
Question 10.
What happens when [NCERT]
- Dilute sulphuric acid is poured on copper plate ?
- Iron nails are placed in copper sulphate solution ? Write word equations of the reactions involved.
Answer:
- When sulphuric acid is poured on copper plate, copper sulphate and hydrogen gas are produced.
Copper + Sulphuric acid ——-> Copper sulphate + Hydrogen (gas). - When iron nails are placed in copper sulphate solution, iron sulphate and copper are formed.
Iron + Copper sulphate ——-> Iron sulphate + Copper
Question 11.
Saloni took a piece of burning charcoal and collected the gas evolved in a test tube. [NCERT]
(a) How will she find the nature of the gas ?
(b) Write down word equations of all the reactions taking place in this process.
Answer:
(a) The nature of gas can be found by passing it lime water, which will turn milky.
Question 12.
List different uses of metals that you come across in everyday life.
Answer:
Metals are used for making
- machinery
- automobiles, aeroplanes, trains, etc.
- pins, cooking utensils, electrical gadgets.
- electrical wires.
- thin sheets used for wrapping of food items, medicines, etc.
Question 13.
Choose appropriate words from the brackets and complete the statements.
- Noble gases are found in (free state/compound forms).
- Non-metals are generally (malleable/brittle).
- Potassium after combustion will form (acidic oxide/basic oxide).
- (Iodine/bromine) has antiseptic properties.
- German silver has (copper/silver) as major constituent.
Answer:
- Free state
- Brittle
- Basic oxide
- Iodine
- Copper
Question 14.
State whether the following statements are True or False :
- Sodium is more reactive than magnesium.
- Magnesium reacts with cold water.
- All metals exist in solid form at room temperature.
- Gallium has a low melting point.
- Gold is alloyed with copper to make it hard.
Answer:
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
Question 15.
From among the set of metals — sodium, zinc, iron, copper, silver, select the following giving equations for each reaction :
(a) Two metals which will liberate hydrogen from water.
(b) One metal which is used to prepare hydrogen gas in the laboratory.
(c) One metal which will displace copper from copper sulphate solution.
(d) One metal which will not displace copper from copper sulphate solution.
Answer: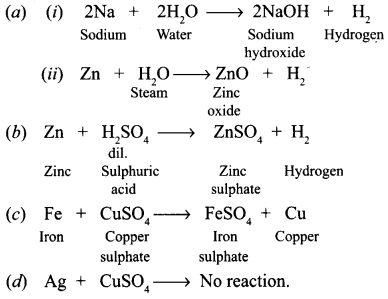
Question 16.
Name one metal which will fit each of the following description. Also write the equation of the reaction.
(a) A metal which floats on water, reacts with it and forms an alkali.
(b) A metal that displaces silver from silver nitrate solution.
(c) A metal which is used for galvanising iron.
(d) A metal that reacts with oxygen without burning.
(e) A metal that bums in oxygen with a bright light.
Answer: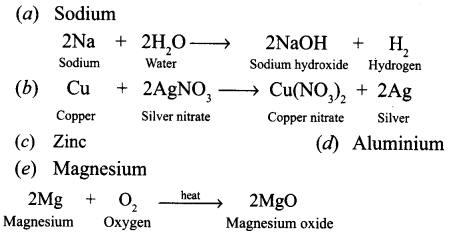
Question 17.
A set of metals in order of their increasing chemical reactivity is given below : silver, copper, lead, iron, zinc, magnesium and sodium.
- Which of the above metals is stored in kerosene ?
- Which metals will react with cold water ?
- Which gas will be liberated when metals react with cold water ?
- Which of the metals will react with oxygen when heated ?
- Which of the metals become black in the presence of hydrogen sulphide ?
Answer:
- Sodium
- Sodium
- Hydrogen
- Zinc, magnesium
- Silver
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 MCQs
Question 1.
Which of the following properties is generally not shown by metals?
(a) Ductility
(b) Sonorous
(c) Dullness
(d) Electrical conduction
Answer:
(c)
Question 2.
The most abundant element in the universe is
(a) hydrogen
(b) oxygen
(c) helium
(d) carbon
Answer:
(a)
Question 3.
The ability of metals to be drawn into wires is known as
(a) ductility
(b) conductivity
(c) malleability
(d) sonorousity
Answer:
(a)
Question 4.
The most abundant element in the earth crust is
(a) iron
(b) oxygen
(c) silicon
(d) aluminium
Answer:
(b)
Question 5.
Galvanisation is a method qf protecting iron from rusting by coating with a thin layer of
(a) silver
(b) galium
(c) zinc
(d) aluminium
Answer:
(c)
Question 6.
The most abundant ihetal in earth crust is
(a) Cu
(b) Al
(c) Fe
(d) Zn
Answer:
(b)
Question 7.
An alloy is
(a) a compound
(b) a heterogeneous mixture
(c) a homogeneous mixture
(d) an element
Answer:
(c)
Question 8.
In extraction of copper, the flux used is
(a) FeO
(b) Si02
(c) CaO
(d) FeSi03
Answer:
(b)
Question 9.
Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of a metal with a metal or non-metal. Which among the following aljoys contain non-metal as one of its constituents?
(a) Amalgam
(b) Brass
(c) Bronze
(d) Steel
Answer:
(d)
Question 10.
Which of the following is purest form of carbon?
(a) Diamond
(b) Graph’ite
(c) Fullerenes
(d) Charcoal
Answer:
(c)
Question 11.
Which among the following alloys contain mercury as one of its constituents?
(a) Alnico
(b) Solder
(c) Stainless steel
(d) Zinc Amalgam
Answer:
(d)
Question 12.
Which of the following methods is suitable for preventing an iron frying pan from rusting?
(a) Applying paint
(b) Applying grease
(c) Applying a coating of zinc
(d) all of these
Answer:
(c)
Question 13.
Generally, non-metals are not conductors of electricity, which of the following is a good conductor of electricity?
(a) Fullerenes
(b) Graphite
(c) Diamond
(d) Sulphur
Answer:
(b)
Question 14.
Food cans are coated with tin and not with zinc because
(a) zinc is costlier than tin
(b) zinc is less reactive than tin
(c) zinc is more reactive than tin
(d) zinc has a higher melting point than tin
Answer:
(a)
Question 15.
Electrical wires have a coating of an insulating materials. The material, generally used is
(a) sulphur
(b) graphite
(c) PVC
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c)
Question 16.
Which of the following non-metals is a liquid?
(a) Sulphur
(b) Phosphorus
(c) Carbon
(d) Bromine
Answer:
(d)
Ch:5 Coal and Petroleum
Question 1.
What are the advantages of using CNG and LPG as fuels?
Answer:
The advantages of using CNG and LPG as fuels are:
- They burn with a smokeless flame and so does not cause any pollution.
- They leave no ash on burning.
- They are easy to handle and convenient to store.
Question 2.
Name the petroleum product used for surfacing of roads.
Answer:
Bitumen
Question 3.
Describe how coal is formed from dead vegetation. What is this process called?
Answer:
Millions of years ago, trees, plants, ferns and forests got buried below the rocks, soil and sand due to natural processes like flooding, earthquake, etc. Slowly, as more soil deposited over them, they were compressed. This led to the conditions of high pressure and heat. These conditions along with the anaerobic conditions turned the carbon-enriched organic matter of wood into coal.
This slow process of conversion of wood into coal is called carbonisation.
Question 4.
Fill in the blanks.
(a) Fossils fuels are ____ , ____ and ____
(b) Process of separation of different constituents from petroleum is called ______
(c) Least polluting fuel for vehicle is ______
Answer:
(a) coal, petroleum, natural gas
(b) refining
(c) CNG
Question 5.
Tick True/False against the following statements.
(a) Fossil fuels can be made in the laboratory.
(b) CNG is more polluting fuel than petrol.
(c) Coke is an almost pure form of carbon.
(d) Coal tar is a mixture of various substances.
(e) Kerosene is not a fossil fuel.
Answer:
(a) False
(b) False
(c) True
(d) True
(e) False
Question 6.
Explain why fossil fuels are exhaustible natural resources.
Answer:
Fossil fuels take millions of years to be formed. They are limited in nature and cannot be replenished easily, once consumed. Hence, they are considered as exhaustible natural resources.
Question 7.
Describe the characteristics and uses of coke.
Answer:
Characteristics of coke: Coke is 98% pure carbon. It is a tough, porous and black substance. It pro-duces a very little smoke.
Uses of coke: Coke is very useful as fuel. It is a good reducing agent. It is widely used in metallurgical processes to reduce metals from their oxides. It is used for producing water gas.
Question 8.
Explain the process of the formation of petroleum.
Answer:
Petroleum is formed by the burial of aquatic plants and animals below the sea bed. The marine animals and plants died thousands of years ago and settled down in the bottom of sea. In anaerobic conditions, microorganisms decompose this organic matter. Due to high pressure and heat, the dead remains of tiny plants and animals were slowly converted into petroleum.
Question 9.
The following table shows the total power shortage in India from 2004-2010. Show the data in the form of a graph. Piet shortage percentage for the years on the y-axis and the year on the x-axis.
| S. No. | Year | Shortage (%) |
| 1 | 2004 | 7.8 |
| 2 | 2005 | 8.6 |
| 3 | 2006 | 9.0 |
| 4 | 2007 | 9.5 |
| 5 | 2008 | 9.9 |
| 6 | 2009 | 11.2 |
| 7 | 2010 | 10.0 |
Answer:
Coal and Petroleum Class 8 Science NCERT Intext Activities Solved
Activity 1 (NCERT Textbook, Page 56)
Make a list of various materials used by us in daily life and classify them as natural and man-made.
Solution:
| Natural | Man-made |
| Air | Clothes |
| Sunlight | Plastics |
| Water | Fan |
| Minerals | Cement |
| Forests | Cosmetics |
Activity 2 (NCERT Textbook, Page 56)
Take some containers. Fill them with popcorn/peanuts/roasted gram/tof¬fees. Divide students into groups of seven each. Further divide each group into three subgroups containing 1, 2 and 4 students. Label them as first, second and third generation respectively.
These sub-groups represent the consumers. As population is growing, second and third generations have larger number of consumers.
Put one full container for each group on a table. Ask consumers of the first generation from each group to consume eatables from the container of their group. Now, ask the second generation consumers from each group to do the same. Ask students to observe carefully the availability of eatables in each container. If something is left in the containers, ask third generation from each group to consume it. Now, finally observe whether all the consumers of the third generation got the eatables or not. Also observe if anything is still left in any of the containers.
Solution:
Students should perform this activity themselves in their classroom.
Question 1.
Name the petroleum product used for surfacing of roads. [NCERT]
Answer:
Bitumen.
Question 2.
What is the slow process of conversion of dead vegetation into coal called ?
Answer:
Carbonisation.
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks : [NCERT]
- Fossil fuels are ……, ……. and ……..
- Process of separation of different constituents from petroleum is called ………
- Least polluting fuel for vehicle is ………..
Answer:
- coal, petroleum, natural gas
- refining
- CNG.
Question 4.
Tick True/False against the following statements : [NCERT]
- Fossil fuels can be made in the laboratory. (T/F)
- CNG is more polluting fuel than petrol. (T/F)
- Coke is almost pure form of carbon. (T/F)
- Coal tar is a mixture of various substances. (T/F)
- Kerosene is not a fossil fuel. (T/F)
Answer:
- False
- False
- True
- True
- False
Question 5.
Explain why fossil fuels are exhaustible natural resources. [NCERT]
Answer:
Fossil fuels are exhaustible natural resources because they will be exhausted by human activities as they are limited in nature.
Question 6.
What are natural resources ?
Answer:
Material obtained from nature are called natural resources
Question 7.
Classify the following as exhaustible and inexhaustible natural resources- air, sunlight, water, forests, wildlife, coal.
Answer:
Exhaustible resources – forests, wildlife, coal
Inexhaustible resources – air, sunlight, water.
Question 8.
Define carbonisation.
Answer:
The slow process of conversion of dead vegetation into coal is called carbonisation.
Question 9.
What name is given to the process of heating a substance in absence of air ?
Answer:
Destructive Distillation.
Question 10.
How is coke obtained ?
Answer:
Coke is obtained by heating coal in the absence of air.
Question 11.
How is coal tar formed ?
Answer:
When destructive distillation of coal is done, the vapours which condense in the water form coal tar.
Question 12.
Why is petroleum called a fossil fuel ?
Answer:
Petroleum is called a fossil fuel as it is obtained from the bodies of dead organisms.
Question 13.
How is natural gas formed ?
Answer:
Natural gas is formed below the earth’s surface. It is formed above the petroleum.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 5 – 2 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write down any four amorphous forms of carbon. [KVS 2008]
Answer:
Amorphous forms of carbon – coal, charcoal, coke and lamp black.
Question 2.
Explain the process of formation of petroleum ? Name two places in India where it is found.
Answer:
Petroleum is formed by the decomposition of aquatic plants and animal remains. In India, petroleum is obtained from oil wells in Assam and Bombay High.
Distinguish between inexhaustible and exhaustible natural resources.
Answer:
Exhaustible resources – forests, wildlife, coal
Inexhaustible resources – air, sunlight, water.
Question 4.
Why are coal and petroleum known as fossil fuels ?
Answer:
Coal and petroleum are formed from the dead remains of living organisms that is why they are called fossils fuels.
Question 5.
Give two characteristics of coal.
Answer:
Coal is hard and is of black in colour.
Question 6.
Define destructive distillation. Name the residue formed by destructive distillation of coal.
Answer:
Destructive distillation is the process of heating a substance in absence of air. Coke is formed by destructive distillation of coal.
Question 7.
What is meant by refining of petroleum and where is it done ?
Answer:
The process of separating the different fractions of petroleum is known as refining and it is carried out in a refinery.
Question 8.
Give two uses of diesel.
Answer:
Diesel is used as fuel for heavy motor vehicles and in electric generators.
Question 9.
How can petrol be used ?
Answer:
Petrol can be used as a motor fuel, aviation fuel and as solvent for dry cleaning.
Question 10.
How can bitumen be used ?
Answer:
Bitumen can be used for making paints and for surfacing the roads.
Question 11.
Why is petroleum also knbwn as ‘black gold’ ?
Answer:
Due to its great commercial importance, petroleum is known as ‘black gold’.
Question 12.
Can we make coal and petroleum in the laboratory from dead organisms ?
Answer:
No, their formation is a very slow process and conditions for their formation cannot be reached in the laboratory.
Question 13.
Give two disadvantages of using fossil fuels.
Answer:
Fossil fuels cause air pollution and global warming.
Question 14.
Why should the fossil fuels be used with care ?
Answer:
If we use fossil fuels carefully, it will result in better environment, less risk of global warming and they will be available for a longer period.
Question 15.
What is meant by fractional distillation ? What is the principle on which it is based ?
Answer:
Petroleum is mixture of various hydrocarbons having different boiling points. As the number of carbon atoms increase, the boiling point also increases. This property is used to separate the different components of petroleum and is known as fractional distillation.
Question 16.
Name some places in India where natural gas has been found.
Answer:
In India natural gas is found in Tripura, Jaisalmer and in the offshore of Mumbai and in Krishna Godavari delta.
Question 17.
Give two advantages of judicious use of energy ?
Answer:
The advantages of judicious use of energy are :
- It will delay the energy crisis.
- It will give the scientists more time to develop more efficient alternate sources of energy.
Question 1.
Define the term fossil fuel. Name two fossil fuels. [KVS 2008, 2005]
Answer:
Fossil fuels are formed from dead remains of living matter over millions of years when they remained buried under the earth. Coal and petroleum are two fossil fuels.
Question 2.
State one use of each of the following : [KVS 2007]
- Charcoal
- Bone Charcoal
- Coke.
Answer:
Use:
- Charcoal : Fuel.
- Bone Charcoal : Purification of brown coloured sugarcane juice in the manufacture of sugar.
- Coke : Used as a reducing agent in the extraction of metals.
Question 3.
- Name the products obtained when coal is heated in the absence of air.
- Write any two uses of its products. [MSE (Chandigarh) 2007]
Answer:
- Coke is formed when coal is heated in absence of air.
- Coke is used :
- As a fuel.
- As a reducing agent in the extraction of metals.
Question 4.
(a) Give the full form of
(i) LPG
(ii) CNG.
(b) How is petroleum gas obtained ? [MSE (Chandigarh) 2007]
Answer:
(a) (i) LPG — Liquefied Petroleum Gas.
(ii) CNG — Compressed Natural Gas.
(b) Petroleum gas is obtained during fractional distillation of petroleum.
Question 5.
Draw diagram to show petroleum and natural gas deposit.
Answer:
Question 6.
What are ‘Petrochemicals’ ? Give the uses of petrochemicals obtained from petroleum.
Answer:
Petrochemicals are useful substances obtained from petroleum. They are used in the manufacture of detergents, fibres, polyethylene and other plastics.
Question 7.
Name some places where natural gas is found in India. How many reserves are of natural gas ?
Answer:
In India, natural gas has been formed in Tripura, in the Krishna Godavari delta. In India, there are over 100 billion cubic metre reserves of natural gas.
Question 8.
Describe characteristics and uses of coke.
Answer:
Characteristics of coke are :
- it is tough.
- it is porous
- it is pure form of carbon.
Coke is used for extraction of metals and in the manufacture of steel.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 5 – 5 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
- What is CNG ? Give its one use.
- From which natural substance are liquid fuels formed ?
- Which gas is the main constituent of LPG ?
- How was petroleum formed in nature ?
- Why do green leaves not catch fire easily ? [DAV2007]
Answer:
- CNG — Compressed Natural Gas. It is used as a fuel.
- All liquid fuels are formed from petroleum.
- Butane is the main constituent of LPG.
- Petroleum was formed by the sedimentation of dead remains of microscopic marine plants and animals, which were buried under the surface of the earth, millions of years ago.
- Green leaves do not catch fire easily because they contain moisture.
Question 2.
- How have fossil fuels been formed ?
- Why are fossil fuels non-renewable sources of energy ?
- Why is smelling agent added to LPG ?
- Give one reason why LPG is a better fuel than coal.
- Give one advantage of modem chullah over traditional chullah. [DAV 2006]
Answer:
- They have been formed by decomposition of pre-historic plants and animals buried under the Earth’s crust millions of years ago.
- Fossil fuels are non-renewable sources of energy because once exhausted they cannot be re-created in a short period of time.
- Smelling agent is added to LPG to detect the leakage of gas as LPG is colourless and odourless gas.
- LPG is a better fuel than coal because :
- It does not cause pollution.
- It has high calorific value.
- It has low ignition temperature. (Any one)
- Advantages of Modem Chullah over Traditional Chullah :
- High efficiency.
- Causes less pollution.
- Consumes less fuel.
Question 3.
The following table shows the total power shortage in India from 1991-1997. Show the data in the form of a graph. Plot shortage percentage for the years on Y-axis and the year on the X-axis. [NCERT]
| S. No. | Year | Shortage (% age) |
| 1 | 1991 | 7.9 |
| 2 | 1992 | 7.8 |
| 3 | 1993 | 8.3 |
| 4 | 1994 | 7.4 |
| 5 | 1995 | 7.1 |
| 6 | 1996 | 9.2 |
| 7 | 1997 | 11.5 |
Answer: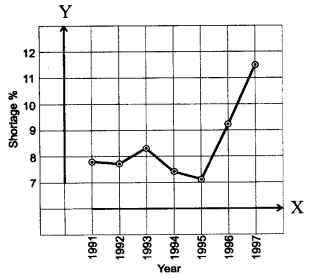
Question 4.
Name the agency in India who advises people how to save petrol/diesel. What tips are given by them ?
Answer:
In India, the Petroleum Conservation Research Association (PCRA) advises people how to save petrol/diesel while driving.
Their tips are :
- Drive at a constant and moderate speed.
- Switch off the engine at traffic lights.
- Ensure correct tyre pressure.
- Ensure regular maintenance of the vehicle.
Question 5.
Draw a labelled diagram showing the fractional distillation of petroleum. Give the uses of any three fractions.
Answer: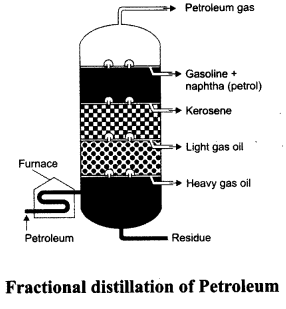
Uses:
- Petrol is used as motor fuel, airation fuel and as solvent for drycleaning.
- Kerosene is used as fuel at home and in jet aircrafts.
- Diesel is used as fuel for heavy motor vehicles and electric generators.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 5 MCQs
Question 1.
Wind, sun and hydropower are
(a) renewable
(b) non-renewable
(c) synthetic sources
(d) none of these .
Answer:
(a)
Question 2.
The unit of calorific value of combustion of fuels is
(a) kilojoule
(b) joule
(c) kilojoule/kilogram
(d) kilogram
Answer:
(c)
Question 3.
A brownish-black sedimentary rock is known as
(a) charcoal
(b) coke
(c) coal
(d) coal tar
Answer:
(c)
Question 4.
Peat is a type of
(a) charcoal
(b) coke
(c) coal
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c)
Question 5.
The most pure form of carbon fuel is
(a) coal
(b) coke
(c) charcoal
(d) coal gas
Answer:
(b)
Question 6.
The fossil fuel found below the sea is
(a) petrol
(b) petroleum
(c) kerosene
(d) diesel
Answer:
(b)
Question 7.
‘Black gold’ is another name for
(a) coal
(b) coke
(c) charcoal
(d) petroleum
Answer:
(d)
Question 8.
The white semi-solid fraction of petroleum used for making vaseline is
(a) asphalt
(b) lubricating oil
(c) paraffin wax
(d) fuel oil
Answer:
(c)
Question 9.
Out of the following, which fuel is best used in the homes ?
(a) Wood
(b) CNG
(c) LPG
(d) Kerosene oil
Answer:
(c)
Thanks it was nice I got help for you 😊😊
ReplyDelete"Earth's fever needs urgent treatment."global warming
ReplyDelete